The RBI has issued guidelines for fair practice code for lenders aimed at protecting the interests of the borrowers. These guidelines are applicable to both banks and financial institutions. Here is a detailed explainer of these guidelines.
Extending loans is the major business activity of Banks & NBFCs. The competition pushes these lending institutions to adopt different means to attract the borrowers. In this process there could be instances where the Banks or other financial institutions are opaque or resort to practices that may give them undue advantage and can infringe on the benefits of the burrower.
In order to curtail such practices and protect the rights of the burrower, the RBI has something known as the ‘Guidelines for Fair Practice Code for the lenders’, which these lending institutions need to follow.
RBI guidelines for lenders aimed at safeguarding the interest of the borrowers
RBI first issued these ‘Guidelines on Fair Practice Code for Lenders’ on 05 May 2003. These guidelines are applicable for all the Scheduled Commercial Banks and all the Financial Institutions in India.
- The guidelines were developed by RBI on the basis of the recommendations of Working Groups on Lenders Liability Laws, which was constituted by Government of India.
- RBI held consultations with the Government as well as few select Banks & Financial Institutions.

The guidelines issued by RBI are categorized under five heads covering different aspects of loan lending process.
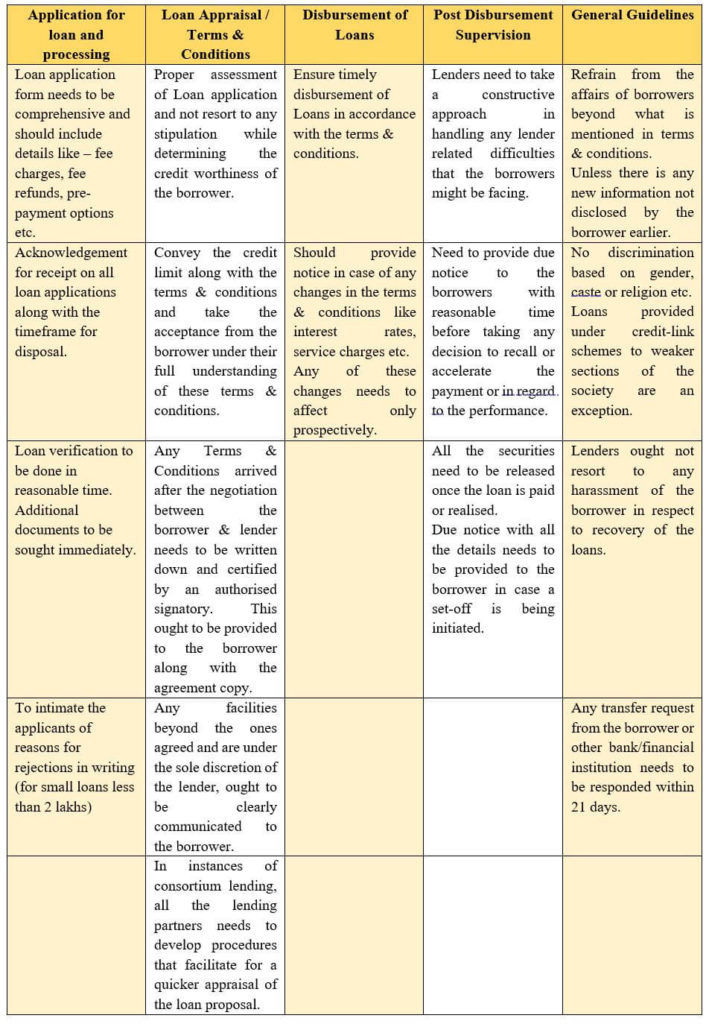
RBI revised these guidelines multiple times
RBI has from time to time conducted a review of the implementation and practice of these guidelines and have suggested revisions. Here is a look at the various revisions to the guidelines that were advised by RBI.
Date | Revisions Advised |
The advice to develop comprehensive loan application form to include all the details, is now extended to all types of loans irrespective of the amount of loan. (Earlier it was less than Rs.2 lakhs). The lenders were required to provide a written letter to the borrowers the reasons for declining a loan. Earlier the limit was Rs. 2 lakhs, now its extended to loans of all amounts. | |
In the initial guidelines, it was advised that any Terms & Conditions or Caveats negotiated between the lender and the borrower needs to be written down and a certified copy with the authorized signatory needs to be provided to the borrower along with loan documents. Few banks used to do it based on the request. RBI has identified that not providing this document is against the Fair practices and has hence mandated the provision of this document as compulsory. | |
RBI has asked banks disclose the information of all the fees and charges that are levied on the customers. RBI has noticed instances where in there were certain additional charges by the Banks & Financial Institutions which were not disclosed earlier. They are now directed to compulsorily include all the details in the comprehensive loan agreement and also inform customers the “all-in-cost”. | |
This revision was issued as a continuation of the earlier one passed in 2008 regarding the disclosure of all the fees and charges in a transparent manner. RBI has re-iterated this and has advised the Banks and Financial Institutions to proactively and transparently disclose all this information, so that the borrowers are in a better situation to compare the different options available across the board. RBI has advised such information to be updated on the respective website for all the loan products. | |
Through this circular, RBI has reiterated the transparency in provision of information. For this it advised banks to do the following. – The website should disclose the information relating to: Interest rate of all the contracted loans, Bank Charges and fees, Annual Percentage Rate (APR) etc.– Banks are required to provide a Key Statement/Fact Sheet to all individual borrowers at every stage of loan processing. A standard format is prescribed for this. |
Fair Practice Code developed by Individual Banks based on RBI’s guidelines
RBI has advised the below actions for all the banks and financial institutions to be implemented after these guidelines were issued.
- All the Banks & Financial institutions need to draft their own Fair Practices Code. They have the freedom to develop and enhance the scope of the document, but care needs to be taken that there is no infringement on the underlying spirit of the guidelines provided. This Fair Practices Code would require the approval of the Board of Directors.
- The Fair Practices Code ought to be put up on the respective websites and needs to be publicized extensively.
- A grievance redressal mechanism needs to be kept in place to resolve any disputes. These disputes need to be promptly reviewed and disposed.
- A periodical review of the compliance to the Fair practices court needs to be conducted by the board of directors and a consolidated report needs to be prepared and submitted regularly.
Accordingly, most of the Banks and Financial institutions have developed their own Fair Practice Code for lenders. This code is put up and can be seen on the websites of the respective banks.
For e.g., the Fair Lending Practices Code (FLPC) of State Bank of India, covers fair practices followed regarding– Product Information, Interest Rates and their revision, Bank Charges, T&C of lending, Accounting practices, Information Security etc. It also developed a Grievance Redressal Mechanism.
Similar Fair Practices Codes can be found for other major banks like Axis Bank, ICICI, Canara Bank etc. along with Financial Institutions like HDFC Credila, Avanse, DHFL etc.
RBI took action on banks & financial institutions who violated this code
The guidelines issued by the RBI and the Fair Practice Codes developed by the Banks is to ensure that the interests of borrowers are protected. There have been instances where the RBI has dealt severely with those who violated the fair practices code.
Recently, in the year 2019, Bajaj Finance Pvt Ltd has been slapped with a fine of Rs.1 crore for violating Fair Practices Code.

In an earlier instance, RBI imposed a fine of Rs. 20 lakhs on Shriram City Union Finance Ltd, for violation of Fair Practices Code. In RBI’s scrutiny, various contraventions were observed which violated RBI guidelines.

On the same day, RBI has charged Hinduja Leyland Finance Ltd with a fine of Rs. 5 lakhs, since it was observed that charging of interest and its communication to the customers was not done in a transparent manner, which is against the Fair Practices Code.

Featured Image: RBI Guidelines for Fair Practice Code


