The Government of India recently released the ‘National Suicide Prevention Strategy’. It is India’s first suicide prevention policy and looks at multi-sectoral collaboration to reduce suicide mortality, through time-bound action plans. Here is a review.
As per the World Health Organization (WHO), more than 7 lakh people die due to suicide every year. It is also the fourth leading cause of death among the 15–29 age group globally in 2019. Nearly 77% of the suicides in 2019, occurred in Low- & Middle-income countries, of which India is one.
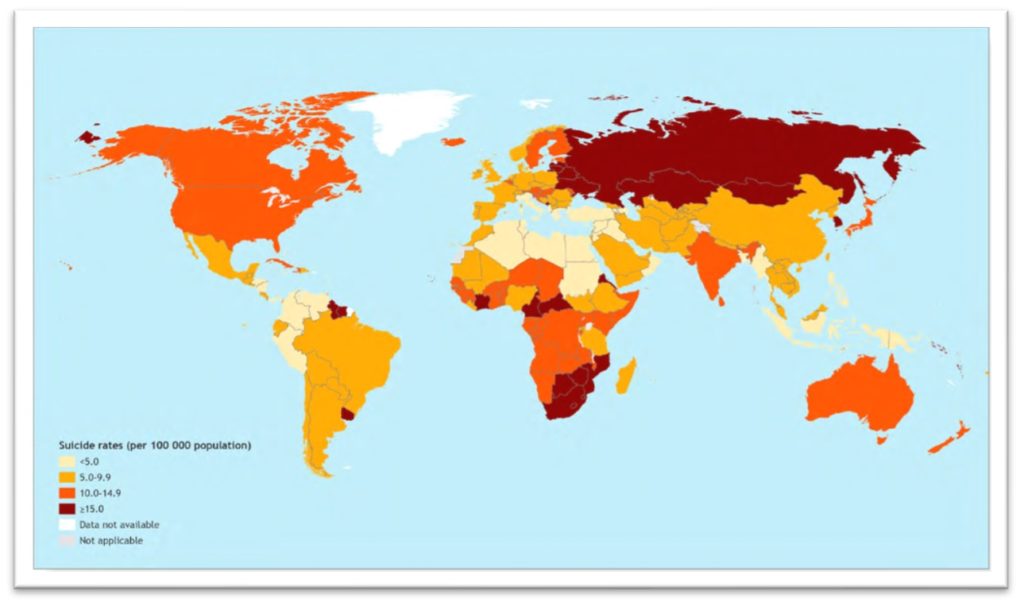
Source: Suicides Worldwide in 2019- Global Health Estimates
WHO recognizes suicide as a public health priority, as stated in its first WHO World Suicide Report – 2014. Accordingly, in WHO Mental Health Action Plan 2013-2030, WHO member states have committed themselves to working towards the global target of reducing the suicide rate in countries by one third by 2030. Also, Suicide mortality rate is an indicator for target 3.4 of Sustainable Development Goals.
As per National Mental Health Survey of India 2015-16, Suicide prevalence in India is 10.4 per 1 lakh population. India is among the countries with a high burden of Suicide. As per Suicides Worldwide in 2019 report, there were 1.73 lakh deaths due to suicides in India during 2019.
India’s National Mental Health Policy, 2014, identifies prevention of mental disorders, reduction of suicide and attempted suicide as core priority areas. Furthermore, the Mental Healthcare Act, 2017 , brought about necessary changes and progressive clauses in the legislation relating to suicides.
In a continued effort in this direction, the Government of India’s Ministry of Health and Family Welfare recently released “National Suicide Prevention Strategy”. It is India’s first suicide prevention policy and looks at multi-sectoral collaboration to reduce suicide mortality, through time-bound action plans.
Increasing trend of suicides in India
Data from the National Crime Records Bureau’s (NCRB) Accidental Deaths and Suicides in India (ADSI) indicates an increasing trend in the number of suicides as well as rate of suicides in recent years. After a declining trend in the rate of suicides until 2017, the suicide rate has increased from 9.9 (per 1 lakh population) in 2017 to 12 in 2021. Factly’s detailed analysis of the trends in suicides in India can be read here. Compared to females, the increase in the suicides is more prominent among the males. Data also indicates that the unemployed and daily wagers account for a major share of the suicides in the country compared to those in a gainful employment.
The ‘National Suicide Prevention Strategy’ report highlights that suicide is the number one cause of death among those aged 15-29 years. Family problems and illness contribute to the highest number of suicides. Furthermore, India contributed 36.6% of the global suicide deaths in 2016. This share was 25.3 % in 1990.

A complex phenomenon influenced by several interacting factors
The report highlights the complex nature of suicide. In most of the cases, several interacting factors like – personal, social, psychological, cultural, biological, and environmental factors contribute to the risk of suicides. Various risk factors are identified which have the potential to aggravate the risk of suicide.
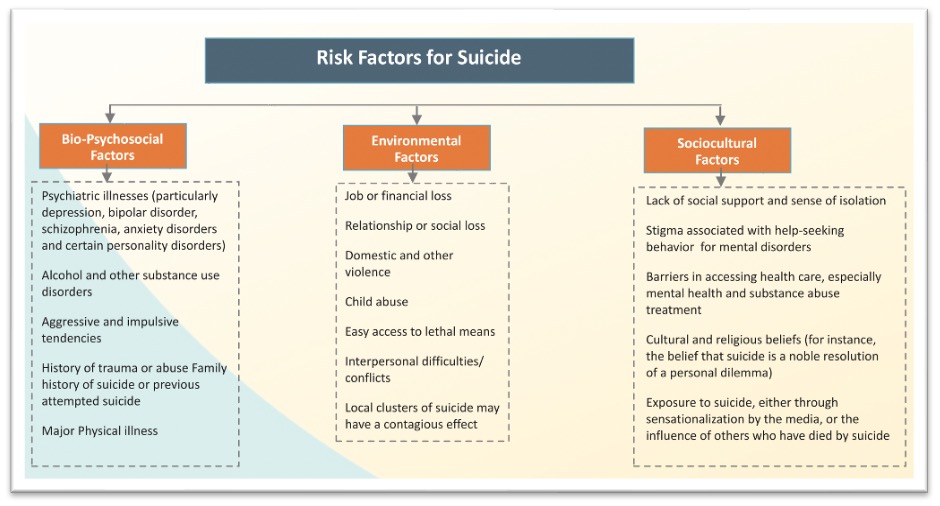
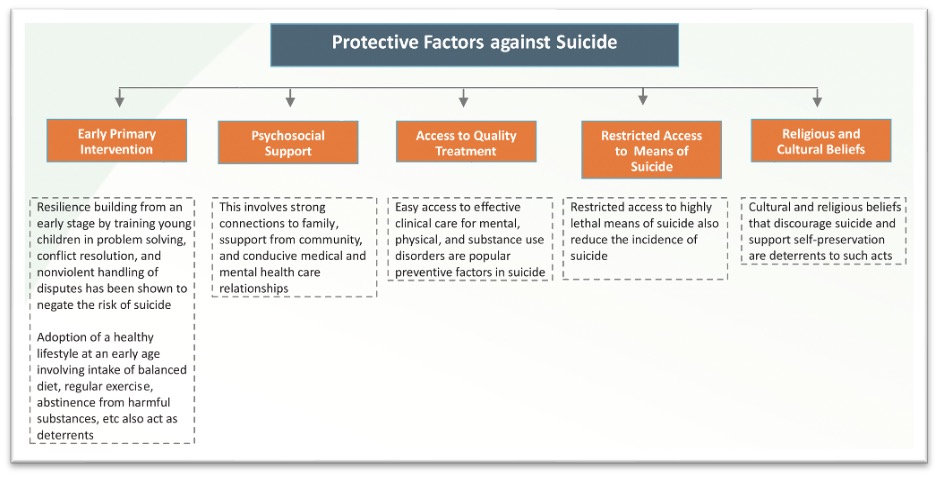
Apart from these risk factors, the report identified the protective factors which can mitigate the risk of suicide. These factors form a key part of the National Suicide Prevention Strategy developed by Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW). Early primary intervention, access to psychological support and quality treatment are the key factors influencing the support systems and infrastructures to be developed as part of the suicide prevention strategy. Surveillance is another aspect that has been identified to be the key in developing the strategy. From India’s perspective, the current data on suicides is limited. Information such as means used or common methods used for suicide is incomplete.
Strategy delineates REDS path for Suicide prevention
The National Suicide prevention strategy laid down the REDS path for suicide intervention. This includes:
- Reinforce leadership, partnerships, and intuitional capacity.
- Enhance the capacity of health services to provide prevention services.
- Develop community resilience and societal support.
- Strengthen surveillance and evidence generation
These form the four key objectives to be achieved through the development and implementation of the strategy. The main objective targeted to be achieved through reinforcing leadership and partnerships is to develop a system in place which will effectively reduce easy access to suicide modes. By enhancing the capacity of the health services, the strategy aims at build specialist mental health workforce. It identifies a host of stake holders to provide support and prevent suicides including – police, teachers, political & faith leaders, volunteers, etc. Increasing community resilience as well as developing societal support are other key components of the strategy.
As indicated earlier, the availability of suicide related data is not complete. Hence the strategy identifies developing surveillance mechanism as another important objective.
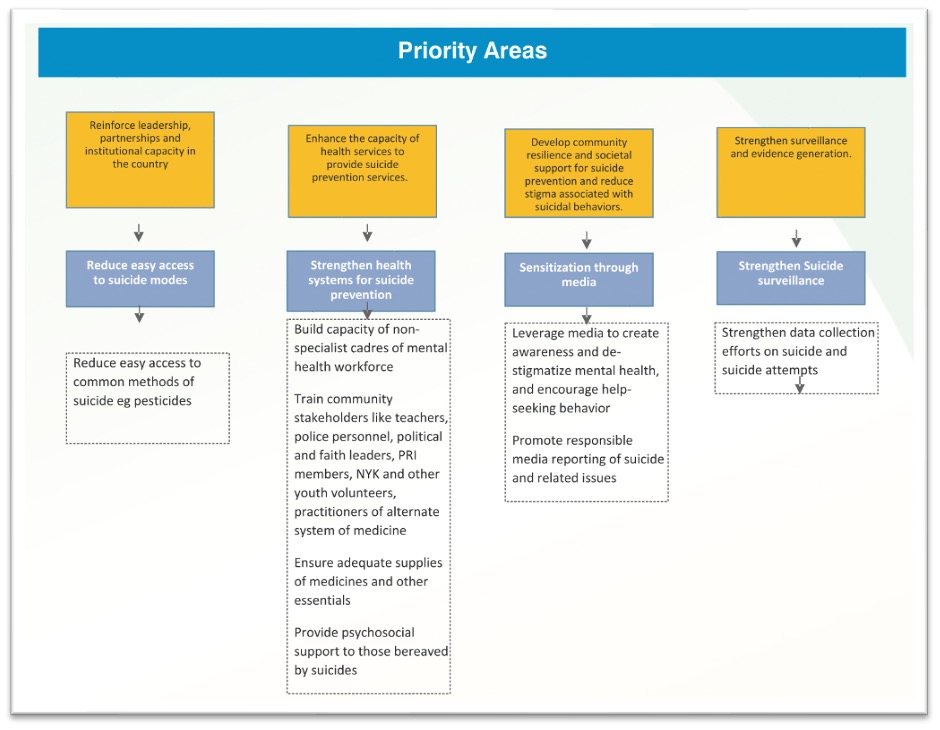
The REDS path also concurs with the multiple interventions that were delineated by the National Mental Health Policy to prevent suicides. Identification of multiple priority areas and following a multi-sectoral approach is an important component of the Strategy.
Different stakeholders and sectors are made part of the suicide prevention strategy. This includes multiple levels of government – Central, State, local self-government, etc. along with other institutions like NGOs, UN Agencies, Educational institutions, corporates, researchers etc.
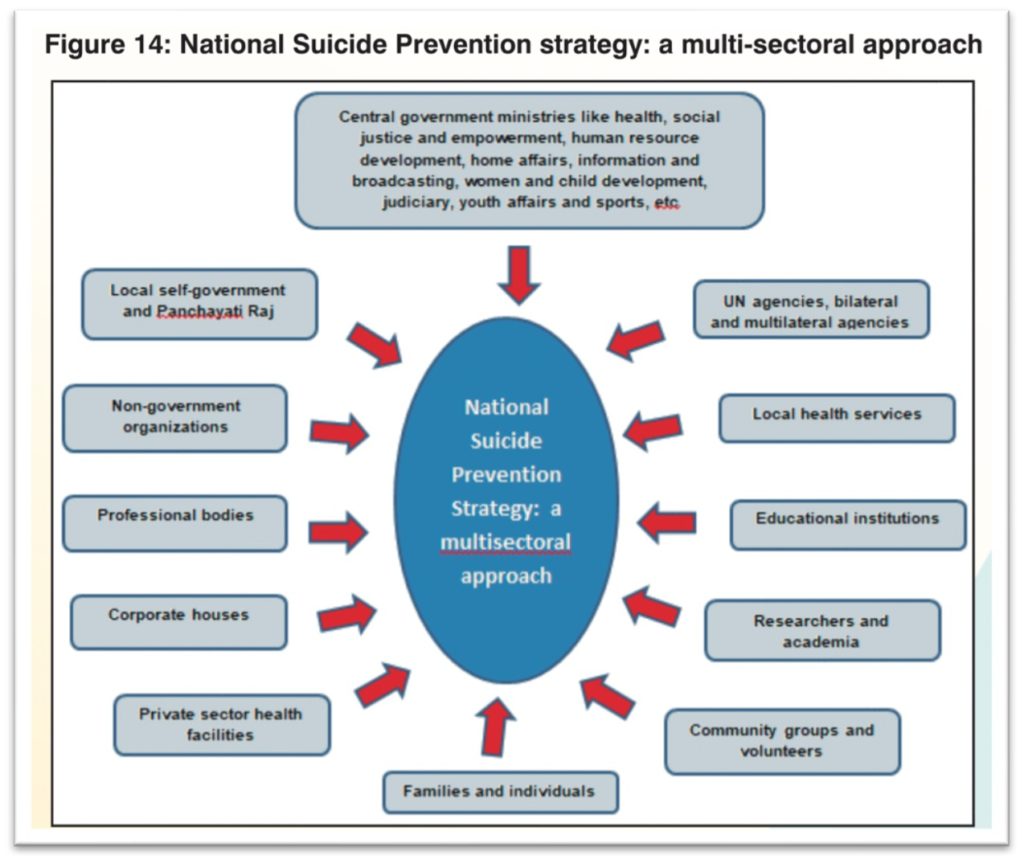
5 key Stake holders identified as part of Implementation framework
An action framework and implementation plan are important for the successful implementation of any strategy. Accordingly, action framework forms the core of this national strategy. It ought to be noted that the national strategy being developed is in accordance with WHO’s Southeast Asia Regional strategy on suicide prevention. The action plan includes the following components:
- Strategy: Detailing the specific strategy to be followed for achieving the state objectives by 2030.
- Action: Outlining the specific steps that needs to be undertaken to achieve the objectives.
- Indicators: Specified the benchmarks to be achieved at regular intervals as part of achieving the final objective.
- Key Stake holders: identifying key stake holders for implementation and achievement of the said objectives.
- Timeline: Defining the timeframe to achieve each of the indicators. Accordingly, the timelines were set at – Immediate, Intermediate and Long-term.
Five key stake holders were identified as part of the National Strategy for prevention of suicides, to implement and achieve the objectives. These include:
- National Level Ministerial Stakeholders.
- State Level Governmental Stakeholders.
- District Level Governmental Stakeholders
- NIMHANS, Bangalore & other apex mental health institutes
- Strategic collaborators.
National level stake holders include Ministry of Health and Family welfare, Ministry of Education, Ministry of Women & child development, Ministry of Information & Broadcasting, Ministry of Youth etc. among others.
At State level, the initiatives are led by Secretary, Health of the respective states. The secretary along with the State Nodal Officer for the National Mental Health Programme is also responsible for the implementation of the strategy at district level, by coordinating with the district level officers. The report provides a detailed framework of the different objectives and the role to be played by each of the stakeholders along with the timelines.
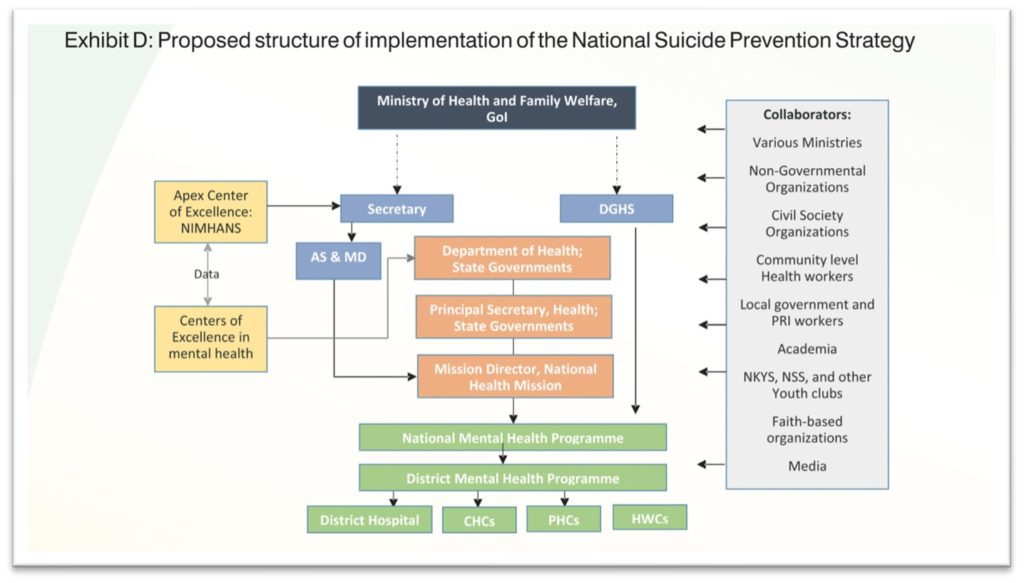
The report identifies – stigma surrounding mental health, limited skilled resources and coordination and collaboration with multiple stake holders as few of the main challenges in implementation of National Suicide Prevention Strategy.



