If one follows news regularly, they will come across words such as inflation, consumer price index, and so forth. There are various types of price related indices such as WPI, CPI, CFPI. Here is an explainer on what they mean.
Whether you go to buy groceries from the store or buy your favourite snack, more often than not, you will notice that the prices have changed. More importantly, if you have followed the news lately, you must have come across words such as inflation, consumer price index, and so forth. But what are these? Why are these necessary? How are these measured? What do they indicate? We will break it down in today’s story.
What and why of macroeconomic indicators
The performance of the economy impacts all of us. Policymakers and economists analyse economic performance by closely following the macroeconomic indicators and determining the likely contractions and expansions in the near future. These indicators target specific areas of the economy, thereby providing a comprehensive picture of the state of the economy.
The economic significance, statistical adequacy, and consistency in the availability of the data are considered to be the key criteria in choosing the right indicators. In India, the Consumer Price Index (CPI), Wholesale Price Index (WPI) and Index of Industrial Production (IIP) are often talked about when analysing the performance of the economy. We look at these three indicators in this story.
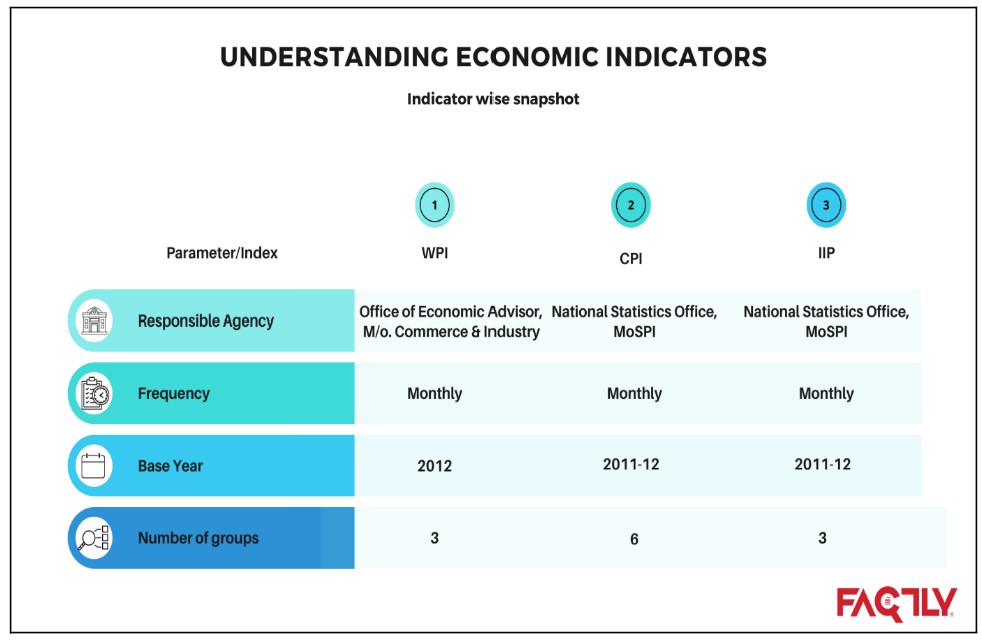
Snapshot of the three indicators
Below is the overview of the three indices.
How is the base year selected?
The primary objective of the base year is to enable inter-year comparisons, thereby giving a fair idea of changes in the parameters. The basic criteria for the selection of base year are as follows.
- Availability of complete and detailed relevant data
- Proximity to the study period
- Normality- a year that is considered typical, or one in which there are no unusual changes to the level of production, trade, prices, or price variations.
- Year of economic significance
- Synchronization with other macroeconomic indicators.
A year fulfilling the majority of the characteristics is chosen as the base year. While the first four criteria have statistical and economic consequences, the last one is for better comparability. The chosen base year is revised periodically to capture the changes in the structure and composition of the industry, and consumption patterns of people and to improve the quality and representativeness of the indices.
Wholesale Price Index (WPI)
The wholesale price index (WPI) represents the cost of goods that are sold in bulk and transacted between businesses as opposed to consumers. The WPI basket is comprised of three major categories- Primary articles, fuel and power, and manufactured goods. The Wholesale Price Index (WPI) number is a measure of the average wholesale price movement for the economy. However, WPI does not cover services.
WPI is often used as a deflator in the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) measurement. It is also used to create escalation clauses for the supply of equipment, construction activities, and raw materials. In long-term sales and purchase agreements, business enterprises frequently include price adjustment (escalation) clauses as a means of managing price increases.
Revision of base-year of WPI
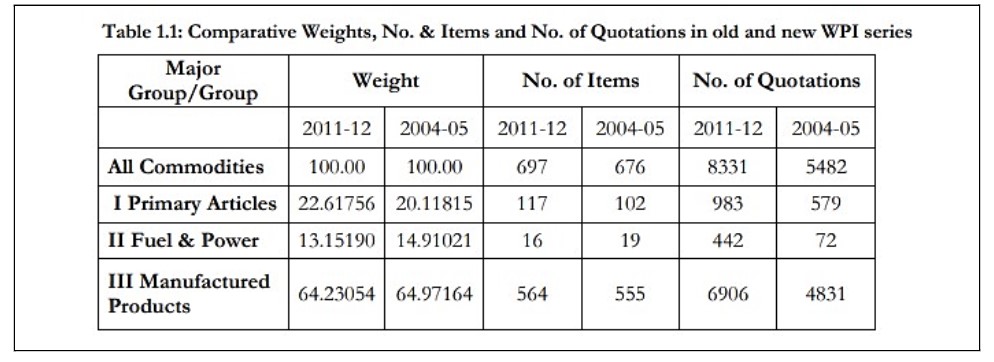
The set of Wholesale Price Index numbers with the base year 2004-05 was introduced with effect from 14 September 2010. Owing to the structural changes in the Indian economy, it was required to update the index basket of the current series of Index numbers of WPI (Base 2004-05=100) and undertake the review of the coverage of commodities, base year, and weighting diagram.
Under the leadership of the late Dr. Saumitra Chaudhuri, a working group for the modification of the wholesale price index numbers (base: 2004-05=100) was established. In accordance with the Working Group’s suggestion for the WPI (Base 2004–05) series revision, a representative commodity basket of 697 items has been chosen.
Below is the comparison of both the base years.
Further, a committee was established in 2019 for the revision of the base year 2011-12. The draft report proposed 2017-18 as the new base year.
Consumer Price Index (CPI)
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) is an index used to track changes in the retail prices of specific goods and services that consumers in a given demographic group spend their money on over time. In practice, a CPI measures the cost of purchasing a fixed basket of goods and services. The coverage and applicability of CPIs are generally limited to specified socio-economic groups.
Below are the types of CPIs are compiled and released at the national level on a monthly basis.
- CPI for Industrial Workers (IW)
- CPI for Agricultural labourers (AL)
- CPI for Rural labourers (RL)
- CPI (General)
- Consumer Food Price Index (CFPI)
Labour Bureau under the Ministry of Labour and Employment compiles the first three while the National Statistical Office under the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation compiles the fourth and fifth indexes.
CPI for Industrial workers:
Since its dissemination began in 1946, this indicator is the most historical of the CPI indexes. It tracks changes in the costs of a set basket of goods and services that Industrial Workers purchase over time. For government personnel, it is used to fix the dearness allowance and index wages. It is currently calculated using 2016 as the base year.
CPI for Agricultural and Rural Labourers:
CPI-AL is basically used for revising minimum wages for agricultural labour in different States. The index is used for determining minimum wages and those for the government’s rural jobs programme under the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act. Currently, CPI-AL/RL with 1986-87 base is available for only 20 states.
Consumer Food Price Index
It is a measurement of changes in the retail cost of food items that a specific population group purchases. Beginning in May 2014, the Central Statistics Office (CSO) provided it in three categories on an all-India basis: rural, urban, and combined. To evaluate price changes for food and their effects on the level of prices generally, it is crucial to measure price movement. It is currently calculated using 2012 as the base year.
Index of Industrial Production (IIP)
The all-India IIP is a composite indicator that tracks short-term shifts in a basket of industrial product output volume over a specified time period relative to a selected base period. The Central Statistics Office (CSO) compiles and releases it each month, six weeks after the reference month.
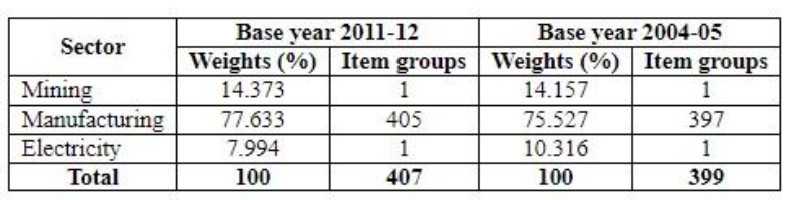
The mining, manufacturing, and electricity sectors are the ones included in the current general index of industrial production due to data availability and other resource limitations.
The base year for IIP was revised from 1993-94 to 2004-05 to 2011-12. Below is the sectoral composition of IIP as per the old and latest base year.
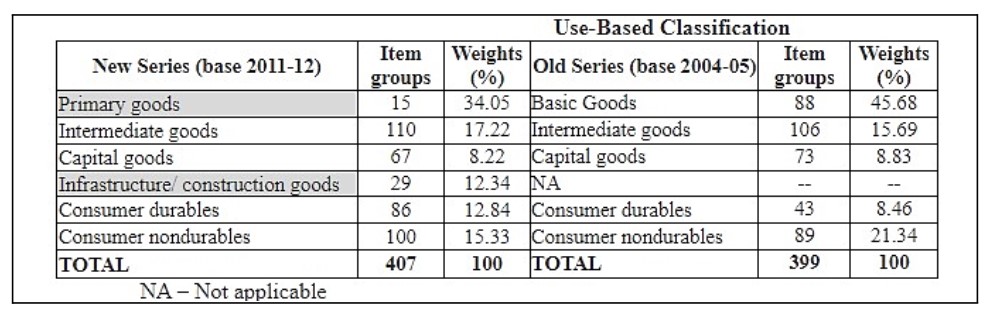
As per the use-based classification in the IIP, below are the changes in weights after the revision of the base year.
The trend in annual growth rates in the IIP is as below.
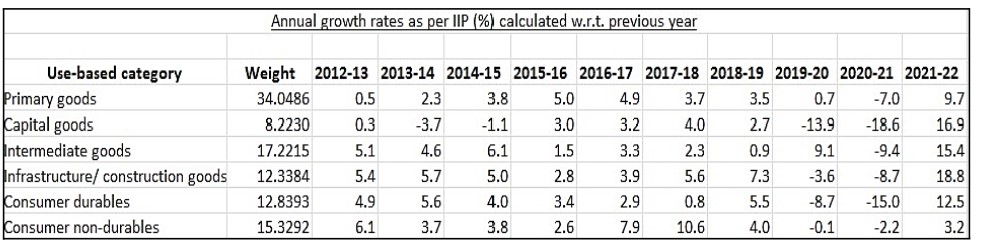
Source: Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation
Featured Image: Inflation-Related Price Indices


