A post is being widely shared on social media claiming that eating grapes (Vitis Vinifera) after taking medicine can cause death. Let’s verify the claim made in the post.
Claim: Eating grapes after taking medicine leads to death.
Fact: While it’s true that certain medicines can have minor to moderate interactions when consumed with grapes or grape-derived products, there is no established scientific evidence to validate the claim that eating grapes after taking medication can result in death. Therefore, the claim made in the post is deemed MISLEADING.
Renowned health authorities such as New Zealand’s Medicines and Medical Devices Safety Authority and WebMD acknowledge that certain foods and fruits, including oranges, pomelos, pomegranates, cranberries, grapes, apples, and grapefruit, can interact with certain medications, potentially inducing side effects.

Specifically, medications metabolized by the liver or those that inhibit blood clotting may experience minor to moderate interactions when consumed with whole grapes, grape juice, or grape pulp. This interaction stems from the possibility that grapes might alter the speed at which the liver metabolizes these medications, consequently modifying their effects and potential side effects. Additionally, the grape extract could potentially decelerate blood clotting. Therefore, consuming grape extract alongside medications that also slow blood clotting might heighten the risk of bruising and bleeding.
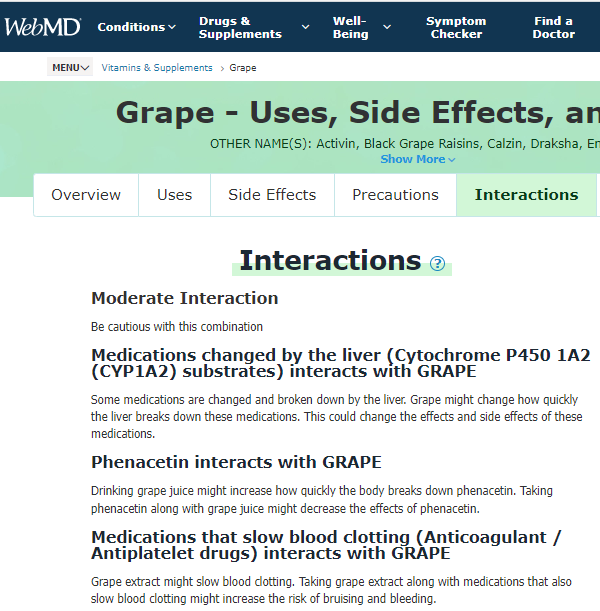
Despite these interactions, there is no established research affirming that consuming grapes post-medication would lead to fatal outcomes. This claim has been consistently dismissed as baseless by numerous medical experts. Nevertheless, as per US FDA, Harvard Medical School, and the National Health Service, there is a notable interaction between several medications and grapefruit (or its juice, extract, or pulp). It’s important to distinguish grapefruit (Citrus × paradisi) from grapes (Vitis vinifera), as they belong to different botanical families.

Grapefruit juice can delay, decrease, or enhance the absorption of certain drugs. It can interfere with the enzymes that metabolize some drugs in the digestive system, resulting in a higher concentration of the drug in the body. This can potentially lead to dangerously high drug levels, causing serious side effects. Additionally, grapefruit can interfere with transporters in the intestines that aid drug absorption, reducing the amount of drug absorbed and potentially diminishing the medication’s efficacy.
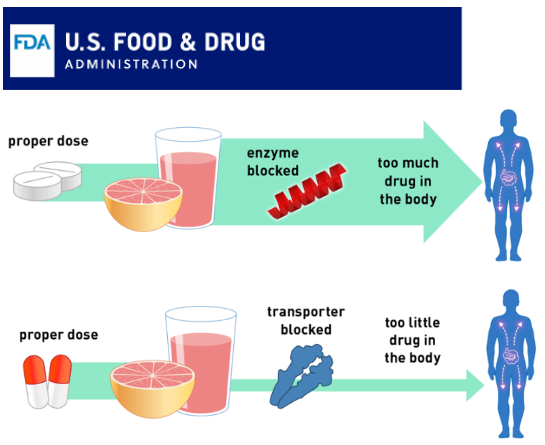
For this reason, it’s crucial always to check the medication’s label and consult with a doctor or pharmacist to understand the potential interactions of the medicines with food items. Being cautious and well-informed can help avoid any unwanted side effects.
In conclusion, there is no scientific evidence to support the claim that consuming grapes after administering medication can result in fatal outcomes.



