‘Best Practices in Social Sector: A Compendium 2023’ was recently released by NITI Aayog in collaboration with the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP). This provides insights into 75 different initiatives that made an impact.
The social sector plays a key role in the overall progress of a society. It encompasses several important components of society – healthcare, Education, drinking water & sanitation, environment, food security, women & child development, livelihoods, social security, skill development, etc. The role of the social sector becomes all the more critical in a progressing country like India to provide equitable opportunities for the marginalised sections of the society to be part of the growth story.
Over the years, the social sector in India has had notable success through various developmental interventions by multiple stakeholders, especially the governments – Central & State. Varied innovations, strategies, plans, schemes, etc. were executed to address many of the challenges across sectors and script success stories. As such, Best Practices in Social Sector: A Compendium 2023, released by NITI Aayog in collaboration with the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), provides insights into such initiatives that have made an impact.
What is this Compendium on Best Practices in Social Sector 2023?
The social sector has witnessed several successful interventions by various stakeholders. In an attempt to document such initiatives, NITI Aayog has collaborated with UNDP and released the “Best Practices in Social Sector: A Compendium 2023”. The aim of this compendium is to highlight impactful, sustainable and replicable models as a reflection on them and to serve as a handbook for future initiatives.
To commemorate the 75th anniversary of Indian Independence, 75 case studies across 14 key social sectors are compiled. The case studies for the compendium are obtained from each State/UT of India along with 30 central government ministries & departments.
The cases identified are across various social sector themes – education, health, nutrition, agriculture, women’s empowerment, sports, financial inclusion, digitization, etc. The compendium contains information about the initiative, its impact & challenges. The information in the compendium is compiled based on the inputs from the respective State/UT governments and ministries.

In this review, we look at a few of the 75 case studies that are part of the compendium. No defined metrics are considered as a criterion for selection with aspects like the scale of impact, the problem being addressed, replicability of the model, etc. being the broader guiding points for selecting a few of these case studies.
Direct benefits, enhancing income among the main drivers for initiatives in Agriculture
About 2/3rd of the population of India is dependent on agriculture and this sector contributes to around 19% of the GDP. It is not only a key component of the social fabric of the country but also to the economy through backward and forward linkages. While dependency on agriculture for livelihood is significantly high, it is riddled with several issues that contribute to financial distress. Outdated technology, the presence of middlemen, lack of infrastructure, etc. are among the challenges plaguing the sector. The initiatives highlighted in the compendium look at addressing a few of these issues.
There are 7 case studies mentioned in the compendium for this sector. Here is a snapshot of a few of them.
Developing value chain for Large Cardamom production in Nagaland: Commercial crops generate a higher revenue than conventional crops. However, the lack of a crop-specific value chain limits farmers to explore this option. Phek Organic Large Cardamom Producer Company, a farmer’s producer company (FPC) with the support of the Department of Horticulture, encouraged the production and developed the value chain for Organic Large Cardamom in the State. Through partnerships between farmers & organic businesses, the revenue generate during 2018-2021 was around Rs. 6.7 crores, with a progressive year-on-year increase. The value chain also created scope for by-products of cardamom fibre.
Crop Cluster development programme in Haryana: This programme initiated by the Horticulture Department of Haryana, aims to provide an on-farm facility to farmers for proper aggregation of the produce, grading/sorting, transportation, and processing of surplus produce during the glut period. A study of two such clusters reveals an increase in the direct income of the farmers through improved market access. Major challenges remain with the professional expertise required for effective market linkages, for which the government has stepped in with its support.
A similar initiative is also launched in Odisha, with a focus on the production of millets and creating a value chain for the produce.
Rice-Fish Farming in Assam: Fisheries department of Assam implemented a pilot of rice-fish farming in 431 hectares of water bodies in 11 districts. This system facilitates a mutualistic symbiosis, where-in fish excreta provides nutrients for the paddy and fish control the pests by feeding on insects eggs & larvae, plankton, etc. This has created an off-season for the farmers and helped in increasing their income without an increase in expenses.
Another initiative is Dr. YSR Rythu Bharosa Kendralu by the government of Andhra Pradesh which provides a one-stop solution for farmers. It works in four verticals – supply of pre-tested quality inputs, capacity building & knowledge dissemination, farmer advisories & call centre, and procurement operations.
Initiatives in Education & Skill Development through Technology and Outreach
The quality of human resources is critical to the progress of any society. This is achieved through education and skill development. The emphasis is evident in the compendium with 11 of the 75 best practices belonging to the education sector and another 5 categorised under skill development.
Efforts for a larger outreach for inclusion of marginalised sections under the fold of formal education and skill development is one of the important aspects addressed in a few of these initiatives.
Scholarship schemes for children of the Tea community in Assam: Children in tribal regions are among the marginalised sections of the society that are deprived of fundamental rights like education, which in turn hampers their future prospects. One such community is the tribal community in Assam which engage in the cultivation of tea. The Directorate of Tea Tribes’ Welfare of Assam launched a set of scholarship schemes to provide scholarships to students from class 9, to facilitate opportunities for encouraging children from the tea community to continue their higher studies, such as MBBS, B.Tech, Ph.D., and other job-oriented courses.
Another initiative in Assam is the School Adoption Initiative in the Darrang district of Assam. Here, each school is adopted by a school teacher to improve the learning outcomes which have been performing poorly in the education dimension.
Few of the initiatives have adopted technology to facilitate- better monitoring, improving quality, outreach, etc. for education and Skill development.
- Vidya Samiksha Kendra (VSK), by the Government of Gujarat, is an online, real-time mechanism to monitor the learning progress of every student across all schools and grades, with the aim to improve grade-appropriate learning outcomes. This initiative received Prime Minister’s Award for Excellence in Public Administration, in 2021 and is also deemed a global good practice by the World Bank.
- Abhyudaya initiative in the district of Dhubri, Assam uses cutting-edge virtual technology to introduce fun-filled ways of learning and better conceptual understanding among students. The district of Dhubri is on the banks of the river Brahmaputra and has many riverine islands. This has contributed to an improvement in learning outcomes with the average scoring percentage increasing from 43% to 65%.
Various best practices related to skill development were focussed on a larger outreach of marginalised and downtrodden sections of society.
- Prayatna, is a livelihood and enterprise training program for transgenders in Delhi-NCR.
- A pilot initiative to enable handloom weavers and local artisans in Sahaspur, Uttarakhand was undertaken to enable market-oriented skills, quality standardization, value addition, branding, better marketing linkages, etc.
Best practices for environment sustainability
Safeguarding and preserving the environment are among the key Sustainable Development Goals. The compendium mentions various best practices that have contributed to this effort.
- Electric Vehicle Policy and introduction of Electrical buses by the Government of Delhi, to reduce emissions from the transport sector and improve air quality.

- Material Recovery Facility (MRF) initiated in Udupi, Karnataka. The programme collects dry waste from homes, which prevents unscientific waste management. The further activity involves identifying materials from this waste and providing them as raw materials for the cement industry.
- Palle Prakruthu Vanam is an initiative by the Telangana government to create dense mini-forests in rural areas.
Interventions for social welfare and women empowerment
Empowerment of marginalised and vulnerable groups, activities promoting social welfare form an integral part of social sector initiatives. There are various programmes and schemes undertaken by Central agencies and State/UT governments which promote social welfare.
- Digital Inspection of Child Care Institutes: In collaboration with Aangan NGO, Punjab’s Department of Social Security and Women & Child Development carries out a digital inspection of its child care institutes through SafCa App. The discrepancies identified during the inspections are colour coded. This allows a better understanding on the functioning of the institutes and allows for improvement.
- Dhimsa Radio: Dhimsa is a Community Radio initiative in Odisha, that facilitates information dissemination to the rural masses. Local language and local youth are being used through this platform to spread government messages to the community.
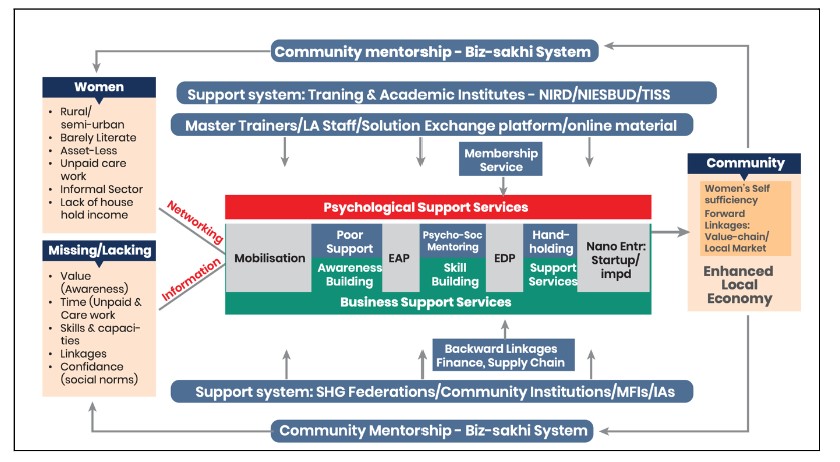
Biz Sakhi: Biz Sakhi aims to improve access to entrepreneurship and employment opportunities for women across rural and urban areas. It provides increased awareness, psychosocial support, enhancing employability, linkages and mentorship support.
Best practices to improve health support
Health is a critical part of social sector services and there are various initiatives across states and by the central government to improve health infrastructure and support across the country.
- STEMI & NSTEMI programme for prompt treatment of heart Attacks: Tamil Nadu government launched ST Elevation Myocardial Infraction (STEMI) and aims to provide free and prompt treatment of coronary artery disease. Data shows that there is an improvement in the quality of acute STEMI care by decreasing the time from symptom onset to hospital arrival and subsequent intervention.
- HBNC+ (Home-based Newborn Care): Pneumonia and Diarrhoea are among the major causes of high infant mortality in Odisha. This is compounded by high levels of undernutrition. HBNC+ is implemented in 3 districts of Odisha. As part of is, there is a follow-up of infants beyond 42 days by ASHAs.