The final week of the 2022 Monsoon Session of the Parliament was marked by fewer disruptions and witnessed debates on important bills. The week’s proceedings were dominated by the farewell to former Vice President & Rajya Sabha chairman Venkaiah Naidu.
The Monsoon Session of Parliament for the year 2022 that commenced on Monday, the 18 July 2022 was adjourned sine die on 08 August 2022. There were a total of 16 sittings spread over a period of 22 days during this session which was originally scheduled to have 18 sittings up to 12 August 2022. The session was curtailed due to the completion of essential Government Business and the demand of members due to gazetting and the Parliamentary holidays.
While the Rajya Sabha held business for over 38 hours, more than 47 hours were lost due to interruptions. The House discussed the issue of rising prices of essential items in the form of a Short Duration Discussion which lasted for more than four hours which 33 Members participated in the debate. Meanwhile, in the Lok Sabha, business was held for 44 hours 38 minutes. The issue of price rise was discussed in the lower house for 6 hours 25 minutes and 32 members participated in the discussion. The productivity of Lok Sabha was approximately 48% and that of Rajya Sabha was approximately 44%.
Key Developments
On the fifteenth day of the session (05 August 2022), both the Houses were adjourned multiple times due to continued protests by the opposition MPs on issues like price hikes, GST, etc. Vice Presidential elections were held this week. Jagdeep Dhankar was elected the 14th Vice President of India.

The farewell of the former Vice President, Venkaiah Naidu was held in the Rajya Sabha on 08 August 2022 forgoing the Zero Hour. In his farewell speech, Venkaiah Naidu stressed on maintaining decency, dignity, and decorum in the House to maintain the image and respect of the House. He also emphasized on giving primacy to the mother tongue by using it in the Parliament, Assemblies, Schools, Administration, Courts, etc.
List of Bills taken up
The Electricity (Amendment) Bill, 2022 which seeks to amend the Electricity Act, 2003 was tabled in the Lok Sabha. The Bill calls for non-discriminatory open access to its network to all other DISCOMs operating in the same area, on payment of certain charges. It also adds that upon grant of multiple licenses for the same area, the state government will set up a ‘Cross-subsidy Balancing Fund’ to finance deficits in cross-subsidy for other DISCOMs in the same area or any other area. Further, the Bill seeks to increase the number of members (including the chairperson) in SERCs from three to four and at least one member in both the CERC and SERCs with a background in law.

The New Delhi International Arbitration Centre (Amendment) Bill, 2022 was introduced and passed in the Lok Sabha. The Bill amended the New Delhi International Arbitration Centre Act, 2019. It also renamed the New Delhi International Arbitration Centre as the India International Arbitration Centre. The bill requires the Arbitration Centre to strive to facilitate the conduct of international and domestic arbitration and conciliation.

‘The Energy Conservation (Amendment) Bill, 2022’ which was introduced in the Lok Sabha previously was passed. The Bill seeks to amend the Energy Conservation Act, 2001 through the establishment of a state energy conservation fund by including a new section 16, and section 14A that authorizes the Union Government, or any agency authorized by it, to issue carbon credit certificates to entities compliant with the requirement of the carbon credit trading scheme.
The Central Universities (Amendment) Bill 2022 that seeks to further amend the existing Central Universities Act, 2009, to establish Gati Shakti Vishwavidyalaya in Gujarat by converting the National Rail and Transportation University, Vadodara was earlier passed in the Lower House. This week, the Rajya Sabha passed the Bill. The Bill also seeks to expand the scope of the deemed university from beyond the railways to cover the entire transport sector to support the ambitious growth and modernization in the field.
The Competition (Amendment) Bill, 2022 was introduced in the Lok Sabha. The Bill seeks to amend the Competition Act, 2002 by proposing institutional changes to make the law in line with the evolving times. The key proposed amendments include expansion of the scope of the combinations to include transactions with a value above Rs. 2000 crores, and a reduction in the time period for approval of combinations from 210 days to 150 days, among others.

During the current Session, a total of 6 Government Bills were introduced. In the Lok Sabha, a total of 7 Bills were passed including the National Anti-Doping Bill, 2022, the Wild Life (Protection), Amendment Bill, 2022, the Central Universities (Amendment) Bill, 2022 and the Energy Conservation (Amendment) Bill, 2022.
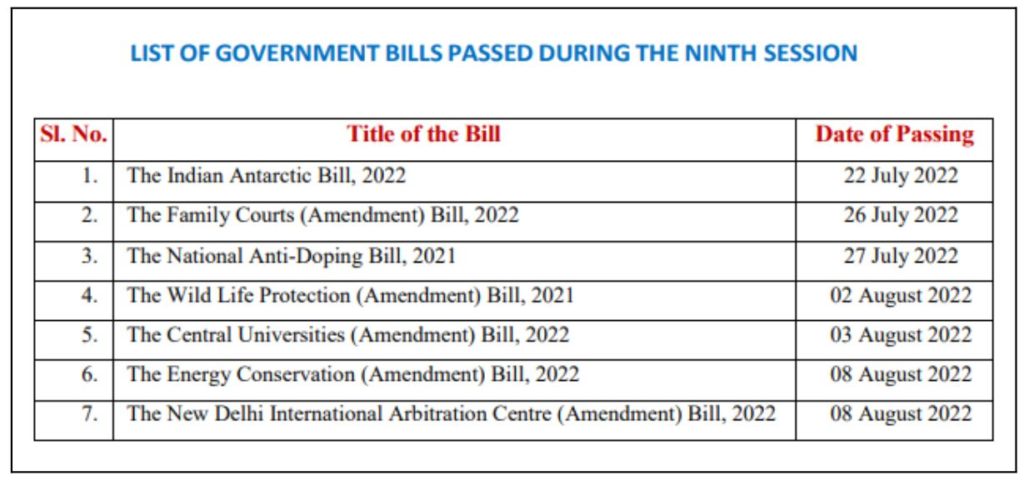
In the Rajya Sabha, only five Bills were considered and passed during the Session. The Five Bills passed by both the Houses are:
- The Weapons of Mass Destruction and their Delivery Systems (Prohibition of Unlawful Activities) Amendment Bill, 2022
- The Indian Antarctic Bill, 2022
- The National Anti-Doping Bill, 2021
- The Family Courts (Amendment) Bill, 2022
- The Central Universities (Amendment) Bill, 2022
Apart from these, Private Member Bills were also taken up in both the Houses. In the Rajya Sabha, the private member’s bill on the Right to Health was discussed partly. During the discussion, the health minister stated that the national budget for health was Rs. 33,000 crores in 2014 when the BJP formed the government which has now increased to Rs. 52,000 crores or by 58% after the BJP Government was formed. Further, the budget has continued to rise with an allocation of Rs 83,000 crores for the year 2022-2023. Some other private bills introduced include the Epidemic Diseases (Prevention, Preparedness and Management) Bill, 2021, the Sal Leaves Collectors and Traders’ Welfare Bill, 2022, the Information Technology (Amendment) Bill, 2022, etc.
Reports tabled
Action Taken by the Government on the recommendations contained in the Eleventh Report of the Standing Committee on Petroleum and Natural Gas (2021-22) on the subject ‘National Gas Grid Including PNG and CNG’ was tabled in the Lok Sabha. Of the 16 recommendations made by the committee, the government accepted 12. The Action Taken Report on ‘Availability of Medicines & Medical devices for COVID Management’ of the Department of Pharmaceuticals under the Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers was also laid.
The Committee on Estimates laid reports on ‘requirement of human capital and physical infrastructure to meet the growth of civil aviation sector in India and development of airports in various parts of the country’, ‘estimates and functioning of National Highway Projects including Bharatmala Projects’, and an action taken report on the ‘recent budgetary reform for better management of government expenditure.’ Apart from these, Action Taken Reports on Demands for Grants 2022-23 for various departments of the Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers were also laid.
Questions raised
In response to a question on homeless people in the country, the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs stated that the number of houseless people in India was 17,73,040 including 9,38,348 from urban areas and 8,34,692 from rural areas, as per the census 2011. It added that in pursuance of the Government’s vision of “Housing for All”, the Ministry is implementing Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana-Urban (PMAY-U) since 2015 for people in urban areas including homeless people. Total assessed demand of houses reported by States under the scheme was 1.12 crores. Further, in the last five years and current year, a total of 1.08 crore houses were sanctioned, 93.5 lakh houses were grounded for construction and 58.17 lakh houses were completed and delivered to the beneficiaries.
A question on crimes against children in orphanages was raised. In response, the Ministry of Women and Child Development stated the figures provided by the National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR). According to NCPCR, 34 complaints were received relating to child abuse/exploitation in Child Care Institutions (CCIs) including orphanages during the last three years. Over 1.4 lakh cases of crimes against children were registered in each of the years 2018 and 2019 and over 1.28 lakh cases were registered in 2020, according to National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB).
Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM) is being implemented since August 2019 to make provision of potable tap water supply to every rural household in the country, by 2024. According to the Ministry of Jal Shakti, when the Mission was announced, 3.23 Crore rural households were reported to have tap water connections. In the last 35 months, 6.70 Crore (35%) households, have been provided with tap water connections. As on 03 August 2022, out of 19.11 Crore rural households in the country, around 9.93 Crore (51.9%) households are reported to have tap water supply in their homes and the remaining 9.08 Crore rural households are planned to be covered by 2024. The Ministry stated these figures in the Upper House in response to a question.
Snippets
- As on 01 January 2022, there were 1472 vacancies in IAS and 864 vacancies in IPS in various States. This is despite the increase in the annual intake of IAS officers to 180 through Civil Services Examinations since 2012.
- On an average, 60,000 vacancies occur for recruitment in all three Defence Services annually, of which around 50,000 vacancies are for Army. Due to COVID-19, recruitment rallies were suspended in the last two years resulting in a shortfall of 1,08,685 jawans in the Indian Army.
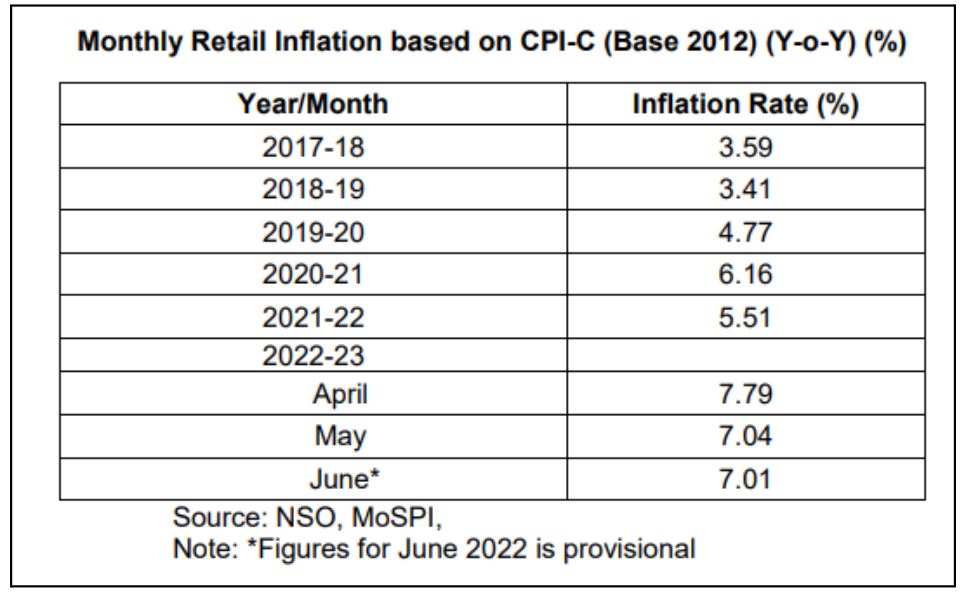
- Wholesale price Inflation based on the Wholesale Price Index (WPI) was 15.18% in June 2022, while the Retail inflation rate based on Consumer Price Index Combined (CPI-C) was 7.01% in June 2022 as compared to 6.26% in June 2021.
- According to RBI, the value of counterfeit notes detected in the banking system has reduced from Rs. 43.47 crores in 2016-17 to Rs. 8.26 crores in 2021-22 while NCRB reported the value of fake currency seized in the years 2017 and 2020 as Rs. 28.10 crores and Rs. 92.18 crores respectively


