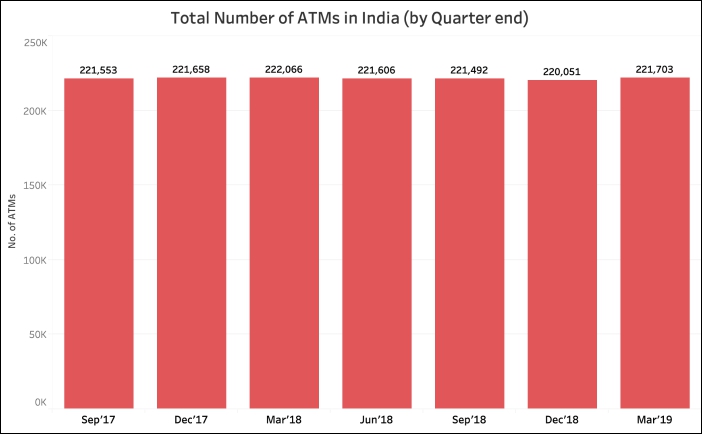
[orc]There were multiple news reports recently about the marginal increase in the number of ATMs in the quarter ending March 2019. But the data of the last 18 months tells a different story. Here are all the details.
The Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) annual report for 2017-18, released in August 2018, points out to the marginal decrease in the number of ATMs across the country. This observation was made by RBI in view of the decreasing trend in the number of ATMs, which further continued until the end of 2018.
However, the previous quarter (Q3 – January to March of Fiscal Year 2018-19) has seen a reversal in this trend where the total number of ATMs in the country have increased from 2,20,051 at the end of Dec’18 to 2,21,703 by the end of March’19, an increase of 1,652 ATMs. These numbers as per the Data Releases by RBI , reflect this trend.
After a steady reduction of number ATMs from 2,22,066 at the end of March’18 to 2,20,051 by the end of Dec’18, the total number ATMs have increased in previous quarter.
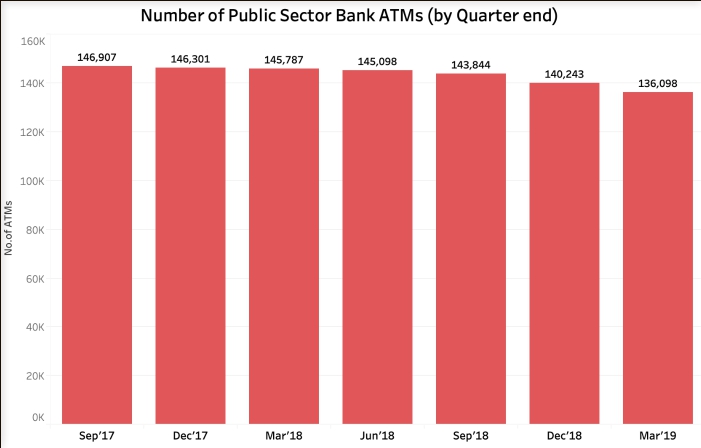
Continued fall in the Number of Public Sector Bank ATMs
While the total number of ATMs have marginally increased in the last quarter, the Public Sector Bank ATMs tell a different story. The number of ATMs of public sector banks across the country have witnessed a continuous decrease over the last 6 quarters.
The number of ATMs of Public Sector banks has reduced from 1,46,301 by the end of Dec’17 to 1,36,098 by the end of March’18. This is a decrease of 10,203 public sector bank ATMs or about 7%. In the previous quarter itself ( Jan’19 to Mar’19) , the number of public sector banks ATMs has come down by 4,145.
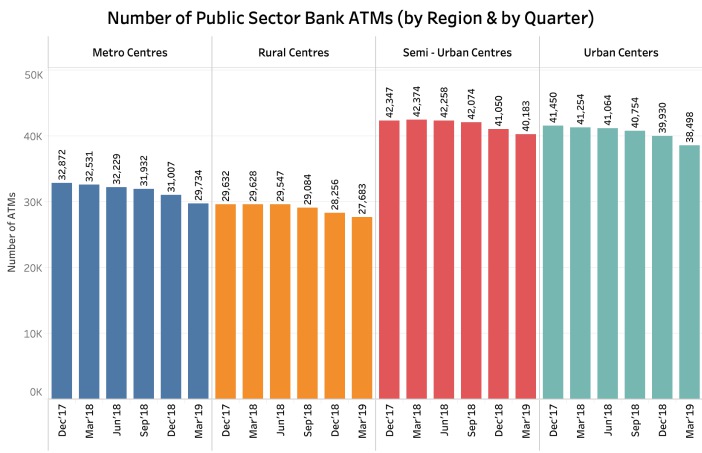
Public Sector Bank ATMs – Decrease uniform across regions
The dwindling number in public sector bank ATMs is a trend observed across the regions – Metro, Rural, Urban and Semi-Urban Centres, as is categorized in the data provided by RBI.
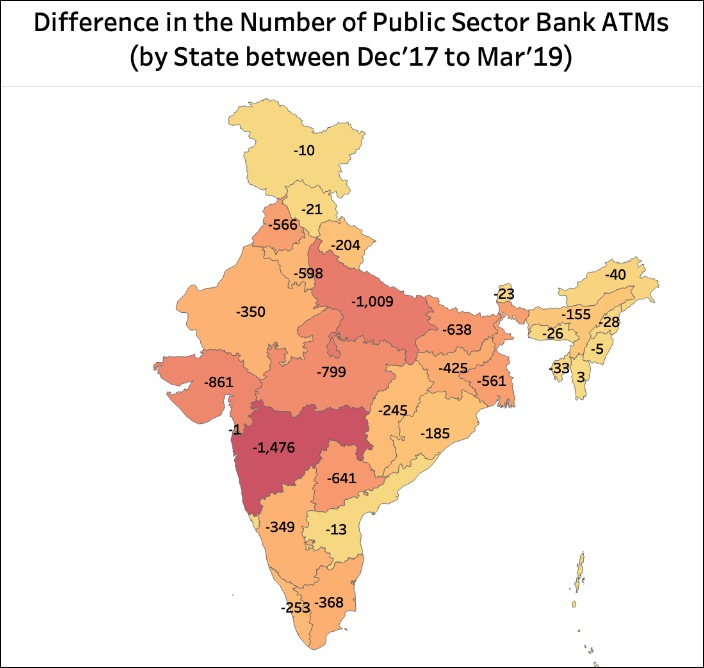
Public Sector Bank ATMs – What about states?
The decrease in the number of public sector banks is observed nearly all the states in the country. Most number of public sector ATMs were closed down in Maharashtra (1476), followed by Uttar Pradesh (1009) , Gujarat (862), Madhya Pradesh (799 ) and Telangana (641) between Dec’17 to Mar’19. The only three places where the number of Public sector bank ATMs increased during this period are Chandigarh (where the number of ATMs increased by 42), Mizoram & Lakshadweep.
Which Public sector bank closed down most ATMs?
While State Bank of India, which is India’s largest public sector bank has seen only a marginal decrease in the number of ATMs over the last 6 quarters, 404 to be precise, the other major public sector banks like Bank of India, Union Bank of India, Central Bank of India, Canara Bank etc. have closed down a large number of their ATMs.
Bank of India have closed down 1563 ATMs over the previous 6 quarters with 1250 ATMs being shut down just during the 6-month period of July-18-Dec’18.
Among the Public sector Banks, Syndicate Bank and Indian Bank are found to be the only exceptions. They have increased the number of ATMs operated by them during this period.
| Name of Bank | Dec’17 | Mar’19 | Difference in no. of ATMs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bank of India | 7717 | 6154 | -1563 |
| Union Bank of India | 7690 | 6650 | -1040 |
| Central Bank of India | 4957 | 3966 | -991 |
| Canara Bank | 9743 | 8851 | -892 |
| Bank of Baroda | 10027 | 9572 | -455 |
| UCO Bank | 2805 | 2358 | -447 |
| State Bank of India | 58819 | 58415 | -404 |
| Punjab National Bank | 9598 | 9255 | -343 |
| Syndicate Bank | 4171 | 4509 | 338 |
| Indian Bank | 3218 | 3892 | 674 |
High maintenance costs are cited as one of the main reasons for public sector banks opting to closing down their ATMs. This is also part of the larger consolidation which the banks are going through, in terms of optimizing their presence and to cut down on overhead costs.
The RBI guidelines with regards to the upgrade of the ATMs, cash loading and Safety may also have contributed towards the increased maintenance costs.
This decline in the number of public sector ATMs has coincided with the rise in the number of Debit cards to 885 million, of which a major share is of Public sector banks. The bank accounts opened through Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) have also contributed to the increase in the debit cards issued. Data as per RBI reports also shows an increase in the number of transactions through ATMs and POS.
This is a 2-part series on the number of ATMs in the country. The second part looks at Private bank & White label ATMs.


