[orc]The UGC grants the autonomous status to colleges that meet a set eligibility criteria. As per the latest data released by UGC, 575 colleges across the country have been granted autonomous status and more than 2/3rd of them are from South India.
The University Grants Commission (UGC) document on the XII Plan profile of higher education in India clearly states that the way to improve the quality of undergraduate education is to the delink most of the colleges from the affiliating structure. It also states that Colleges with academic and operative freedom are doing better and have more credibility. The target set out for the 12th plan period is to make 10 per cent of eligible colleges autonomous by the end of 2017. As per the latest available data, a total of 575 colleges across 23 states have been granted autonomous status by the UGC.
What is an autonomous college?
The system of affiliating colleges to Universities was originally designed when their number in a university was small. The university could then effectively oversee the working of the colleges, act as an examining body and award degrees on their behalf. But with time, large number of colleges has been affiliated to a university adversely affecting the quality of the university. The UGC document for the 12th plan makes a note of the need for reducing the number of colleges affiliated to a university to a manageable size.
The Education Commission (1964-66) recommended college autonomy to achieve academic excellence so that colleges have freedom to decide on curriculum that is both modern and locally relevant. Thus the system of granting autonomous status to various colleges began.
As per the latest guidelines, once a college attains the status of an Autonomous College, it is entitled for the following privileges.
- Freedom to determine and prescribe its own courses of study and syllabi, restructure and redesign the courses to suit local needs
- Prescribe rules for admission in consonance with the reservation policy of the state government
- Evolve methods of assessment of students’ performance, the conduct of examinations and notification of results
- Use modern tools of educational technology to achieve higher standards and greater creativity
- Promote healthy practices such as community service, extension activities, projects for the benefit of the society at large, neighbourhood programs, etc.
The UGC also provides financial assistance to the tune of up to Rs. 15 lakh for Undergraduate Colleges and Rs. 20 lakh for PG and UG Colleges, apart from its regular grants. This assistance is provided for meeting the additional expenses on Guest/visiting faculty; Orientation and re-training of teachers; Re-designing courses and development of teaching/learning material; Workshop and seminars; Examination reforms; Office equipment, teaching aids and laboratory equipment; Furniture for office, classrooms, library and laboratories; Library equipment, books/journals; Expenditure on meetings of the governing body and committees; Honorarium to Controller of Examinations.
What are the eligibility criteria?
The following important criteria are considered among others for identification of institutions for grant of autonomy.
- Academic reputation and previous performance in university examinations and its academic/co-curricular/extension activities in the past
- Academic/extension achievements of the faculty; quality and merit in the selection of students and teachers, subject to statutory requirements in this regard
- Adequacy of infrastructure, for example, library, equipment, accommodation for academic activities, etc
- Quality of institutional management
- National Assessment and Accreditation Council (NAAC) accreditation of ‘B’ grade or above
- Financial resources provided by the management/state government for the development of the institution
- Responsiveness of administrative structure and motivation and involvement of faculty in the promotion of innovative reforms etc.
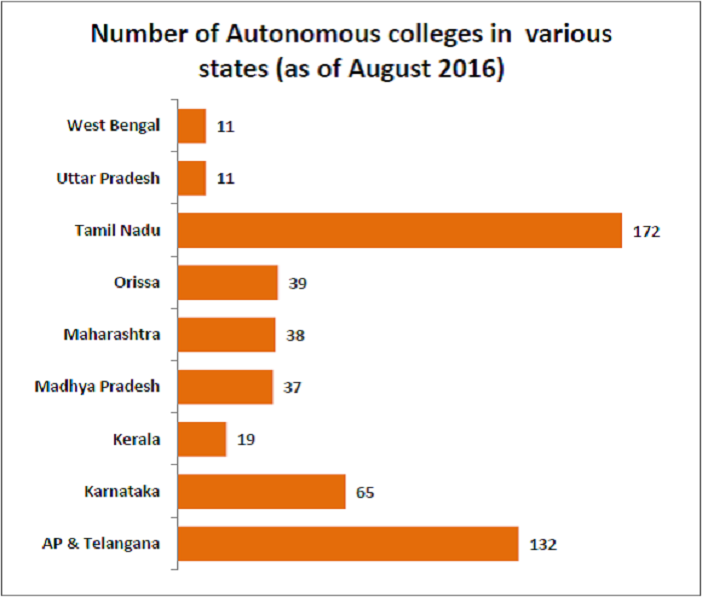
Tamil Nadu has the most number of Autonomous Colleges
Out of the 575 autonomous colleges across the country, 388 of them are from the five South Indian states of Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Karnataka and Kerala. Tamil Nadu has the most number of autonomous colleges followed by AP & Telangana. The 575 colleges are affiliated to 100 different universities. Anna University in Tamil Nadu has the highest number of autonomous colleges affiliated to it. Only 7 universities across the country have more than 20 autonomous colleges each affiliated to them. Five of these are from Tamil Nadu and the remaining two are from Telangana. Out of the 575 autonomous colleges, 164 are government colleges and the rest are not.



1 Comment
Amazing