The NSS 78th Round – Multi-indicator Survey looked at nine ICT skills of the young population between 15-29 years, which are also the skills identified by UNO under SDG-4. The survey results indicate a stark Urban-Rural, and Male-Female divide and this gap increases in higher level skills.
Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) are at the forefront of the technological advancements made by humankind made over the past few decades. It has revolutionised the way people work, interact, learn, and live across various spheres of human life. Skills to use ICT have now become critical in day-to-day functioning to stay connected as well as relevant.
The United Nations Organization has also identified the importance of ICT skills by integrating them into Suitability Development Goals. It is part of SDG-4, which is related to inclusive & equitable quality education and learning opportunities. It has identified 9 activities to measure ICT Skills in persons.

India is one of the leading software & technological service providers globally, but the infrastructure and activity are limited to certain clusters in the country. There is a continuing emphasis on including ICT as part of the educational curriculum. But to what extent of the population is equipped with these skills?
In this context, the recent NSS 78th Round – Multi-Indicator Survey, throws some light. ICT skills of the young population between 15-29 years, were part of the indicators included in the survey. The skills measured were the same 9 activities that were identified by UNO under SDG-4. In this two-part series, we analyse these results of the NSS survey. In the first part of the story, we look at All-India trends.
Methodology
The respondents of the survey are categorised into two age groups for this indicator i.e., 15-24 years and 15-19 years. Gender-wise information and Urban-Rural categorisation are provided in the NSS report. The results are a share of the population within the specific category for each type of skill.
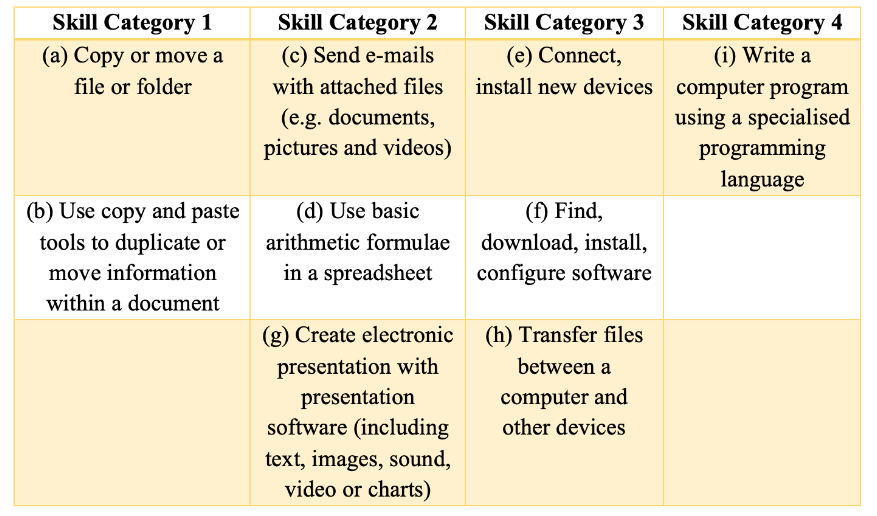
For the purpose of the story, we have divided the 9 skills/activities into four groups based on the level of skill required and the similarity between the activities.
The survey results are based on the responses of the relevant respondents, and no verification was conducted to test the skills.
Only about 1/3rd of Rural population of 15-29 years knows how to Copy or move files and folders
The first two activities under the ICT Skills involve – (a) Copy or moving a file/folder and (b) Using Copy Paste Tools.
There is a distinct rural-urban divide as well as a gender difference in these skills. Around 43% of those surveyed in the age group of 15-24 years know how to copy or move a file. However, this is only about 35.4% among the rural population and 63.1% among the urban population.
In the case of the Urban population, it is 66.7% among males and 59% among females. The difference is starker among the Rural population, with 41.9% among males and 28.4% among females. There is a prominent difference between urban & rural populations across both genders. The proportion nearly remains the same even among those surveyed among the 15-29 age group.
Another skill identified is using copy & paste tools within a document. The proportion of the population survey who reported that they possess this skill was nearly the same as the first skill. Overall, 40.7% of those surveyed between the 15-24 age group had this skill, with about 39.4% among the 15-29 age group. While 61.1% of the Urban population surveyed can use copy-paste tools, it is only about 32.9% among the Rural population. In the case of males, it is 64.7% and 39% among Urban & Rural respectively. In the case of females, it is 57.1% & 26.2%.
Only about 5-6% of those between 15-24 years can use basic spreadsheet & presentation tools in Rural areas
In our next categorization, we look at three skills that require using software applications. The first one is being able to send emails with attachments. 43% of those who were part of the survey between 15-24 years of age can execute this activity. This is 63.1% among Urban respondents and 35.4 % among those from Rural areas. The gender gap is lower among the urban population with it being 59% among females compared to 66.7% among males. But it is starker among the rural population with 41.9% and 28.4% around rural males & females.
Fewer respondents possess the other two skills. Only about 10% of the respondents in the 15-24 years & 15-29 years age group can use Basic arithmetic formulae in spreadsheets. It is 20% among Urban respondents and only 5.8% among rural respondents among the 15-24 age group. It is only slightly higher in those in the 15-29 age group. Compared to the earlier skills, the gender difference is lesser among both urban & rural respondents.
Comparatively, a lesser proportion of the population can prepare a presentation using a presentation software. Overall, 8.4% of the respondents in the 15-24 age group have this skill. It is 17.2% among urban respondents only about 5% among those surveyed in rural areas.
About 20% respondents can install software, with significant Urban-Rural variance
Another set of ICT skills that were part of the survey is related to the respondents’ ability in handling & maintaining the computer systems. These include – connecting & installing new devices, downloading & installing software, and transferring files between computers and other devices.
About 12.4% of the respondents said they can connect and install new devices. While it is 24.1% among urban respondents, it is only about 7.9% among rural respondents. Within the Rural population, it is 9.7% among males and only 6% among females. In the case of females in the 15-29 years age group, it reduces further to 5.5% among rural women.
Comparatively a greater proportion of respondents said they can download, install, and configure software on a device. The overall all-India average among the 15-24 age group is 21.2%. Even within this skill, an Urban-rural divide exists with 34.3% and 16.1% among urban & rural respondents respectively. The share is higher among males in both Urban & Rural areas, with the gender difference being nearly the same.
Among the respondents, 20.3% between 15-24 years said that they can transfer files between computers and other devices. However, it is only about 14.2% of the rural population. It is even lower among rural females with 10.9%. This is comparatively higher among the Urban population with 17.2%.
Only about 2% of the respondents can write a computer program
A more advanced skill among the nine ICT skills is the ability to write a program using specialised programming language. The All-India average is only around 2.2%. Among rural respondents, it is only 1.2%. It is better among Urban respondents with 4.6%. In the case of rural women, only about 0.9% of the respondents stated that they can write a program in both age groups. Among Urban respondents, it is 3.9% in the 15-24 age group.
Rural-Urban divide and gender disparity across ICT skills
As is expected, the All-India numbers from the survey indicate a decreasingly lower proportion of the population possessing a skill based on the level of complexity. While simpler tasks like copying files have a comparatively higher proportion of being able to do them, there is a distinct reduction as far as skills like connecting devices, using software tools, etc, are concerned. It was reduced to 2% in the case of higher-level skills like writing a program.
Another distinct trend is the Urban-Rural divide. There is a large variance, particularly as the complexity increases, with a higher proportion of the urban population possessing the skill compared to rural respondents. There is also a visible gender disparity & divide. Across all the IT skills, the rural woman has the least proportion of such a skill.
In the next part, we look at the trend across the various states of India.
Featured Image: NSS MIS Report


