A post claims that Japan is at the forefront of development & progress because the country believes in Buddhism. The post further claims that the constitution of Japan was adopted in 1287 and that Article 1 of Japan’s constitution is the phrase, which means ‘Buddham Sharanam Gacchami.’ Let’s verify the claim made in the post.
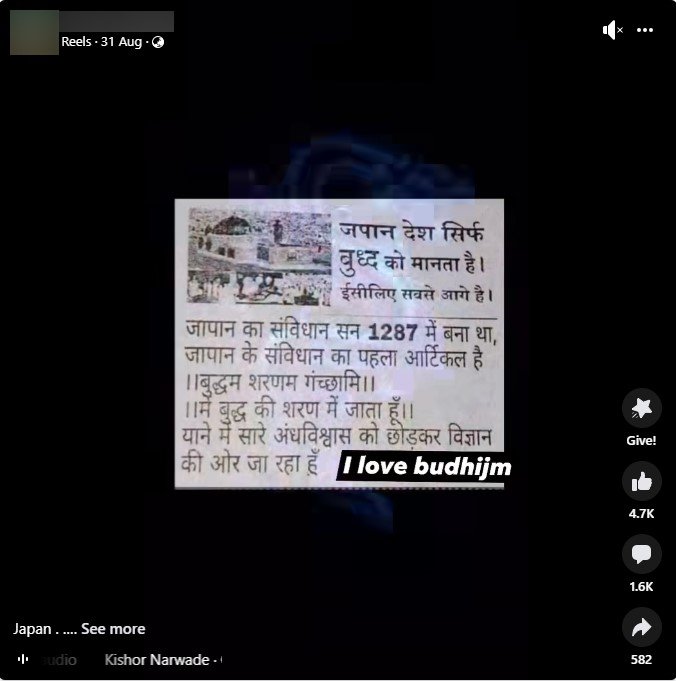
Claim: The Constitution of Japan was adopted in 1278 and Article 1 is ‘Buddham Sharanam Gacchami.’
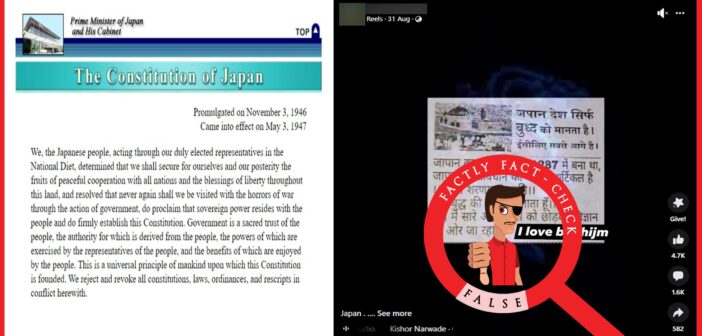
Fact: The constitution of Japan was adopted in 1947 of which Article 1 deals with the fundamental statement about the role of the emperor of Japan. Shintoism and Buddhism are the major religions followed in Japan. Hence, the claim made in the post is False.
When we searched about Japan’s constitution, using relevant keywords, we found that Japan did not have a modern written constitution in the year 1278. In fact, during that time, Japan was ruled by the Kamakura Shogunate, which was a feudal military government. In fact, The constitution was promulgated by Japan only in the year 1946 and it came into force on 3 May 1947.

It is popularly known as the post-war constitution because it was drafted by a team of legal experts within allied forces and not by Japanese leaders as it was enacted in the aftermath of World War II.

During further research regarding the phrase ‘Bhuddham Sharanam Gacchami’, we found that the phrase means, I take refuge in Buddha and that it was not explicitly mentioned not just in Japan’s Constitution but in any constitution. Besides, Shintoism and Buddhism are two major religions that are followed by the Japanese. Further, Article 1 of the Constitution of Japan establishes the fundamental principles of the country. It reads ‘The emperor shall be the symbol of the State and of the unity of the people, deriving his position from the will of the people with whom resides sovereign power.’

The Constitution of Japan consists of eleven chapters. Chapter 1 titled “The Emperor,” deals with the role and status of the emperor which consists of Articles 1-8.
To sum up, Article 1 of the constitution of Japan deals with the fundamental statement about the role of the emperor of Japan, and it was adopted in the year 1947.