The international reaction to Russia’s aggression in Ukraine has been varied though most countries denounced Russia’s actions. In this story, we look at few of the key resolutions & voting results in various international forums regarding the ongoing Russia-Ukraine war.
Russia launched a large-scale military assault on Ukraine on 24 February 2022. This has escalated the already existing hostilities between the two neighbouring countries and has now led to full-scale war.
The relationship between the two former Soviet republics has been strained for quite some time now and particularly since 2014, in the wake of the Revolution of Dignity in Ukraine. This revolution toppled the then President, who refused to sign a political association and free trade agreement with the European Union, a notion which enjoyed the support of a majority of the Ukrainian Parliament. The latest escalation is part of the continued hostilities since 2014 when Russia annexed Crimea from Ukraine.
The international reaction to Russia’s aggression has been varied though most countries denounced Russia’s actions. The complex nature of the diplomatic relations with the countries involved and the humanitarian crisis unfolding in the wake of the military action, has necessitated the international community to respond.
In this story, we look at a few of the key resolutions & voting results in various international forums regarding the ongoing Russia-Ukraine war.
Russia uses its Veto power to block UNSC’s draft resolution
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six main organs of the United Nations. The primary responsibility of the UNSC is maintaining international peace and security. The UNSC consists of 15-members, which includes 5 permanent members and 10 elected members.
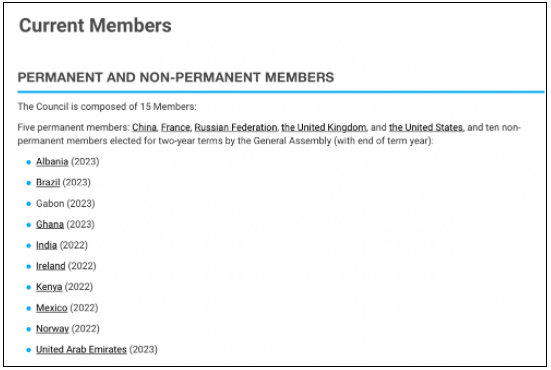
The five permanent members of the UNSC have the ‘Power of Veto’ i.e., the power to stop any resolution. A representative of each of the members of the UNSC is required to be always present at UN Headquarters so that the Security Council can meet at any time as the need arises.
The UNSC can meet whenever there is a threat to international peace and security. Accordingly, in view of Russia’s attack on Ukraine, UNSC sat for a meeting on 25 February 2022. Prior to this meeting, there were two other emergency meetings on 21 February & 23 February. In the wake of the unfolding crisis in Ukraine, Albania and the United States submitted a draft resolution in the UNSC meeting.

The purpose of the draft was to deplore Russia’s aggression, which was in violation of Article 2, paragraph 4 of the UN Charter. The draft also includes the request to immediately cease of force by Russia and to deplore its decision regarding the sovereignty of two regions in Ukraine. The resolution garnered support from 11 members, while 3 countries – China, India & UAE abstained from voting. Russia, which is a permanent member of the UNSC, exercised its power of veto. As a result, the UNSC failed to adopt the resolution.

Security Council vote sets up emergency ‘UN General Assembly’ session
After the failed attempt to pass the resolution in UNSC due to Russia’s veto, UN Secretary-General, Antonio Guterres stated that the UN’s primary objective is to end the war and even though the objective was not achieved in the UNSC meeting, they must never give up.
Accordingly, UNSC met again on 27 February 2022. The purpose of this meeting was to secure approval for setting up an emergency UN General Assembly session.

The text of the draft resolution presented in the UNSC meeting was a procedural one i.e., the calling of the emergency session of the UN General assembly being procedural. Hence, none of the 5 permanent members can veto it. Furthermore, it requires only 9 votes in favour to pass. The measure to convene the General Assembly session was adopted by 11 in favour, 3 – abstaining (China, India & UAE) and Russia voting against it.
UN General Assembly adopts resolution demanding Russia to withdraw all troops
The UN General Assembly (UNGA) is the main policy-making organ of the UN, and it comprises all the member states. It currently has 193 members and each of them has an equal vote.
As per the resolution 377A(V), also called “Uniting for Peace”, adopted by the General Assembly in November 1950, the General Assembly can be convened in case the UNSC fails to exercise its responsibility of maintaining international peace and security, due to lack of unanimity of the permanent members. In such cases, an emergency General Assembly meeting can be convened within 24 hours.

Accordingly, General Assembly convened for an Emergency Special session on 28 February 2022. There were only 10 such earlier instances of emergency special sessions following the adoption of the resolution in 1950.
The Draft resolution presented in the General Assembly:
- Deplores Russia in the strongest terms regarding its aggression against Ukraine.
- Demands Russia to immediately and unconditionally reverse its decision of 21 February 2022, related to the status of certain areas in the Donetsk and Luhansk regions of Ukraine.
- It Demands Russia to immediately cease its unlawful use of force against Ukraine and deplores Belarus’s involvement in this.
- Urges for immediate peaceful resolution of the conflict through political dialogue, negotiations, mediations, etc.
- Demands all the parties allow safe and unfettered passage to destinations outside Ukraine, facilitate unhindered access to those needing assistance in the country, protect civilians, medical & humanitarian workers.
The representative of Ukraine presented the resolution in General Assembly. The draft resolution was adopted by a vote of 141 in favour while 5 member countries voted against the resolution (Belarus, Eritrea, Russia, North Korea & Syria). India is one of the 35 countries that were present but abstained from voting. 12 countries were not present.
UNHRC in its resolution condemned the Human Rights violations
Abuse and violation of Human rights are a direct result of any military conflict. The United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC) adopted a resolution that condemns in the strongest possible terms the human rights violation, abuses and violations of international humanitarian law resulting from Russia’s aggression against Ukraine.
UNHRC is a United Nations body, and its mission is to promote and protect human rights around the world. It has 47 elected members and is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland. As part of the resolution, UNHRC has called for immediate, safe, and unhindered humanitarian access. It has also decided to establish an independent international commission of inquiry to investigate all alleged violations of human rights in the context of Russia’s aggression against Ukraine.

Ukraine presented the resolution on 04 March 2022. A total of 32 members voted in favour of the resolution, while 2 voted against it. 13 member states including India abstained from voting.

European Parliament condemned Russia’s aggression against Ukraine
On 01 March 2022, the European Parliament adopted a resolution regarding the Russia-Ukraine conflict. Since both the countries are European countries, the conflict has a bearing on the rest of Europe. However, it ought to be noted that both the countries are not part of the European Union.
The European Parliament is one of the three legislative branches of the European Union. It consists of 705 members (MEP – Members of European Parliament).
A few of the key aspects of the resolution include:
- Condemn in the strongest possible terms Russia’s illegal, unprovoked, and unjustified military aggression against Ukraine and the involvement of Belarus.
- Demand Russia to immediately terminate military activities in Ukraine.
- Underline Military aggression to be a serious violation of international law.
- Condemn Russia’s use of Belarusian territory.
- Urge continued diplomatic efforts to stop aggression.
- Denounce Russia’s recognition of territories in Ukraine
- Call for sanctions
A total of 637 MEPs voted in favour of the resolution text, 13 voted against it while 26 MEPs abstained.


