[orc]The 71st survey report of the National Sample Survey Office (NSSO) on Health in India reveals that more people are hospitalized today than 20 years ago. The survey also reveals that more women reported ailments than men. Private health care providers were the preferred choice for both the rural and urban population.
The National Sample Survey Office (NSSO) recently released the 71st round report on ‘Health in India’. The report is based on surveys done between January and June of 2014. According to this latest report, about 4.4% of urban population was hospitalized (excluding childbirth) any time during a reference period of 365 days while only 2% urban population was hospitalized according to the 52nd NSSO survey conducted in 1995-96. In the rural areas, 3.5% was hospitalized while this was only 1.3% in 1995-96.
More Urban people reported ailments than Rural
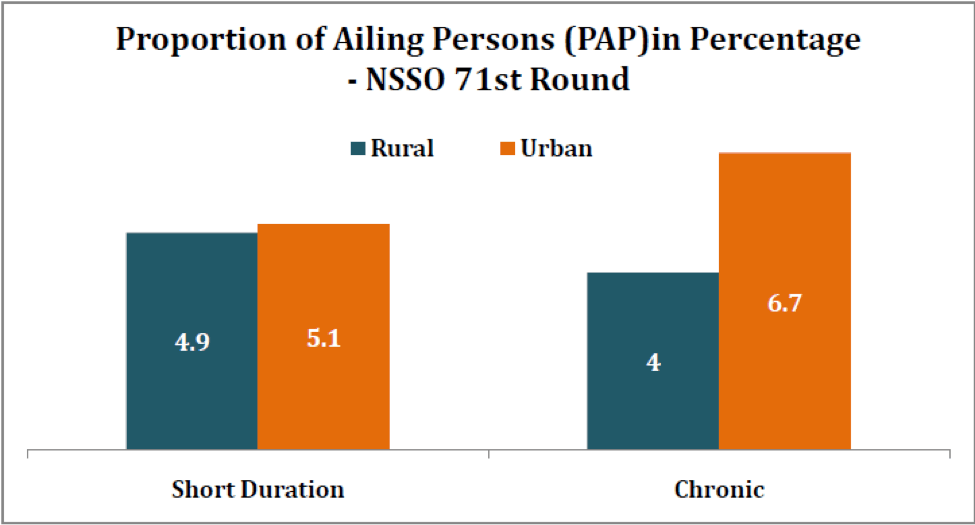
The survey also reports about the Proportion of Ailing Persons (PAP). This is based on self reported illness than any medical examination. The survey notes that this could be an under-estimate of the illness-status of the patients, particularly latent diseases that have not presented with clear symptoms. 8.9% of the rural population reported any ailment in a reference period of 15 days while 11.8% urban population reported an ailment. While there was not much of a difference in the PAP who reported short duration ailment between rural and urban, the difference was evident in the chronic ailments. 6.7% of the urban population reported a chronic ailment as compared to only 4% of the rural population.
More Women reported an ailment than Men
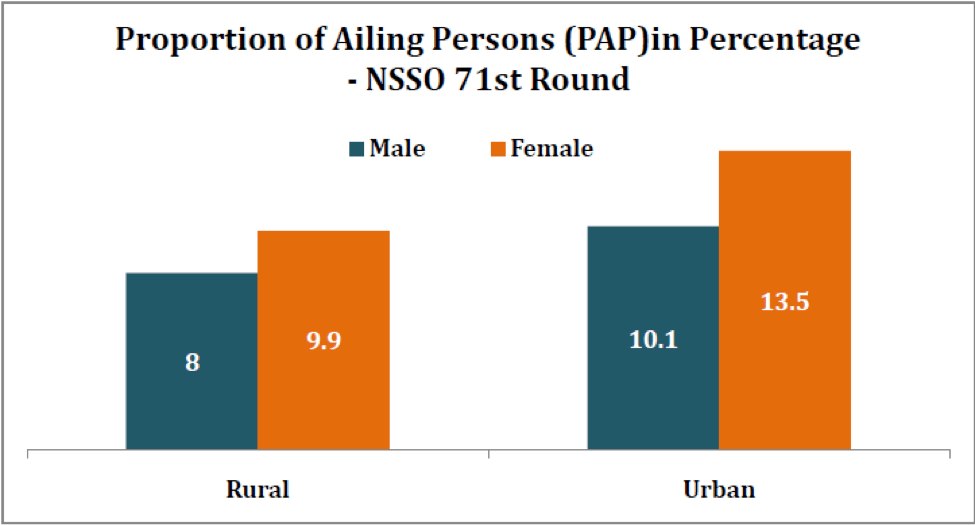
There was considerable difference in the percentage of men and women who reported an ailment during the survey. In the rural areas, 8% of the male population reported an ailment while 9.9% of the female population reported an ailment. This difference was even starker in the urban areas where 10.1 of the male population and 13.5% of the female population reported an ailment.
Kerala reported the highest PAP
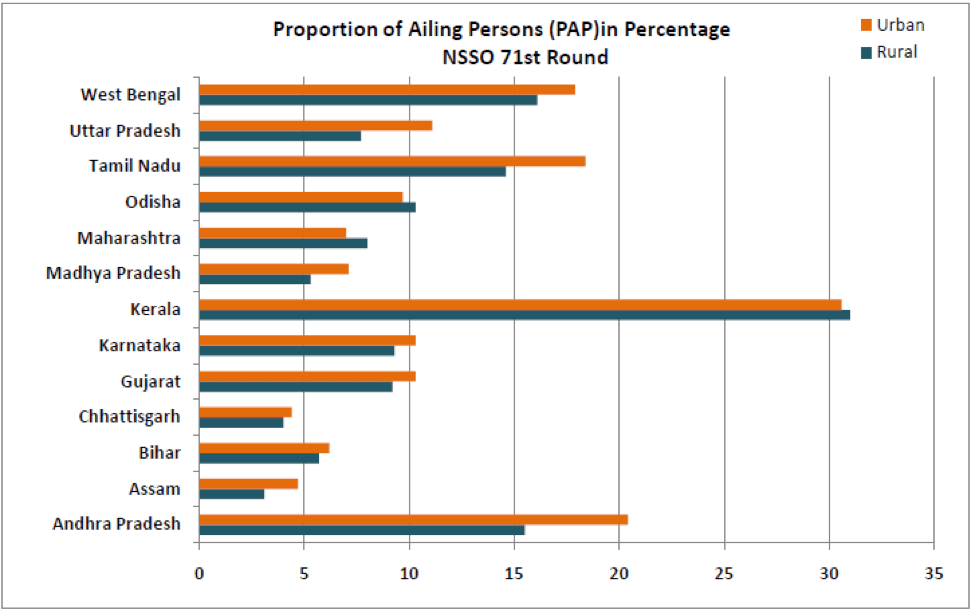
Of the various states covered in this survey, Kerala reported the highest PAP with 31% rural and 30.6% urban population reporting ailments. It has to be noted that the PAP observed in the survey do not reveal the difference in the actual health status but, they confirm the widely held view that self-perceived illness reporting is highly influenced by the literacy rate, cultural context, general health awareness, and access to health care in those states. This could be the reason why Kerala reported the highest PAP while states like Assam, Bihar & Chhattisgarh reported very low PAP.
More than 50% did not take medical advice because of financial constraints
Financial constraint was the most cited reason in this round of the survey for treatment without medical advice. 57.4% of the rural population and 68.3% of the urban population cited this reason. The next most important reason cited was ‘no medical facility available in neighbourhood’ in the rural areas and ‘others’ in the urban areas. Both lack of proper medical facilities in the rural areas and financial constraints remain important reasons for not taking medical advice.
Private is the preferred choice as the healthcare provider
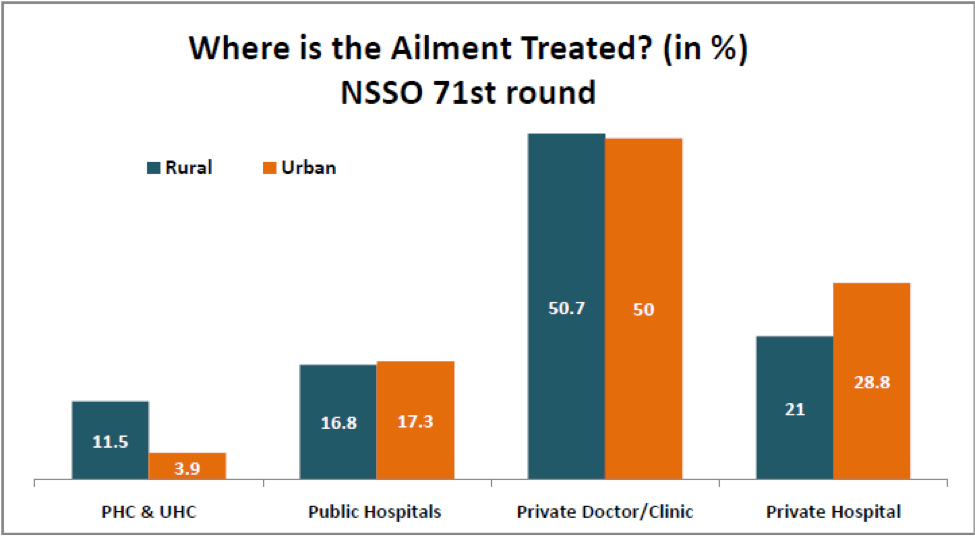
In both rural and urban areas, private health care providers were the preferred choice for a majority of the population. 28.3% of the rural population depended on the public health care providers were the remaining on private providers. In the urban areas, only 21.2% depended on the public health care provider. In both rural and urban areas, Private Doctors/Clinics was the preferred choice for half of the population.