As the number of COVID-19 cases increase sharply across India, the need for medical oxygen is also growing. But what are the different ‘Medical Oxygen’ systems that are used to supply oxygen to those in need? Here is a detailed explainer.
On 28 April 2021, the Government of India released a Press Statement that stated that around 1 lakh portable Oxygen Concentrators would be procured from PM Cares fund. The setting up of 500 more PSA oxygen plants was also announced. These are in continuation of the efforts to ramp up oxygen supply in the country in the wake of a sharp increase in the COVID-19 cases and those requiring oxygen support.

This statement from the government comes after various reports of shortage of medical oxygen across the country in view of treating the increasing COVID-19 cases. The country is in midst of the second wave of COVID-19 surge, with more than 3.5 lakh new cases being reported every day in the last few days. More than 3 thousand daily deaths are also being reported due to COVID-19.
While there is no proper information or data as yet on the number of deaths or complexities in COVID-19 treatment due to lack of oxygen, certain news reports have highlighted this issue.
Efforts are being directed towards increasing the capabilities of both production and supply of oxygen to different parts of the country. Different Medical Oxygen Systems are being deployed in these efforts.
In this story, we take a look at the different oxygen systems available and their specific utility. The World Health Organization (WHO) & UNICEF’s Technical Specification and Guidance for Oxygen Therapy Devices is the guiding document that we have referred to for this story.
Medical Oxygen needs to contain minimum 82% of pure oxygen
While it is a common notion that we inhale Oxygen and exhale Carbon Dioxide, the air that we breathe in contains a mix of several gases – oxygen, nitrogen, hydrogen, carbon dioxide, etc. On the other hand, ‘Medical Oxygen’ is highly pure oxygen, that is used for medical treatment. In this form of oxygen, other types of gases are not allowed in the Oxygen system source, e.g., Oxygen cylinders.
As per the specifications provided by WHO, medical oxygen should contain at least 82% pure oxygen and needs to be free of any other contamination.

As part of meeting the demand, the assistance of few industries is being sought for the production of medical oxygen. For example, the services of Steel Plants like Vizag Steel are being enlisted for this purpose. In most of these industries, Oxygen is used for processes like – oxidation, combustion, chemical reactions, cutting, etc. However, the industrial oxygen has different purity levels and is not appropriate for human use. Hence, they are required to make changes to the composition to produce Medical oxygen.
In its manual, the WHO affirms the key role of Medical oxygen in the treatment of hypoxemia (very low levels of oxygen), in basic emergencies, respiratory illnesses, etc.
Respiratory systems are among the more suspectable body systems to be affected by COVID-19. Hence, medical oxygen assumes importance in the treatment of COVID-19 infected patients. The increase in demand is in proportion to the increasing COVID-19 cases.

Oxygen Concentrators & Oxygen cylinders are among the main Oxygen sources in Low resource Settings
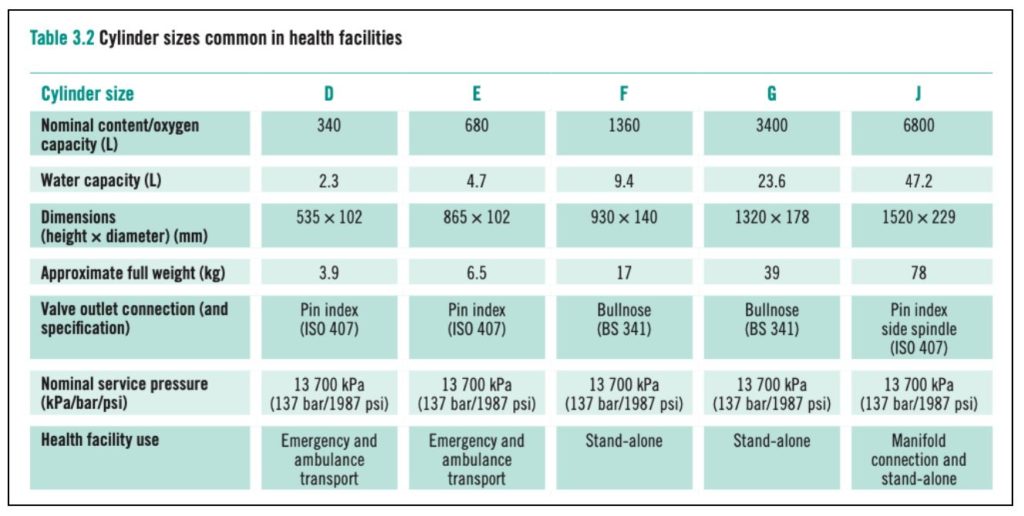
Medical Oxygen is required in various levels of the health system i.e., ranging from Primary Healthcare, emergency transport to Intensive care units (ICUs). The oxygen systems which are required to meet these specific needs also vary accordingly.
Basically, Oxygen system needs to include:
- Oxygen Source – equipment for oxygen production/storage
- Oxygen Distribution
- The mechanism for Oxygen delivery (to the patient)
- Oxygen Monitoring systems.
Different aspects like health facility, available infrastructure, capacity, supply chain, cost, etc. are considered to determine the oxygen system, especially the Oxygen Source.
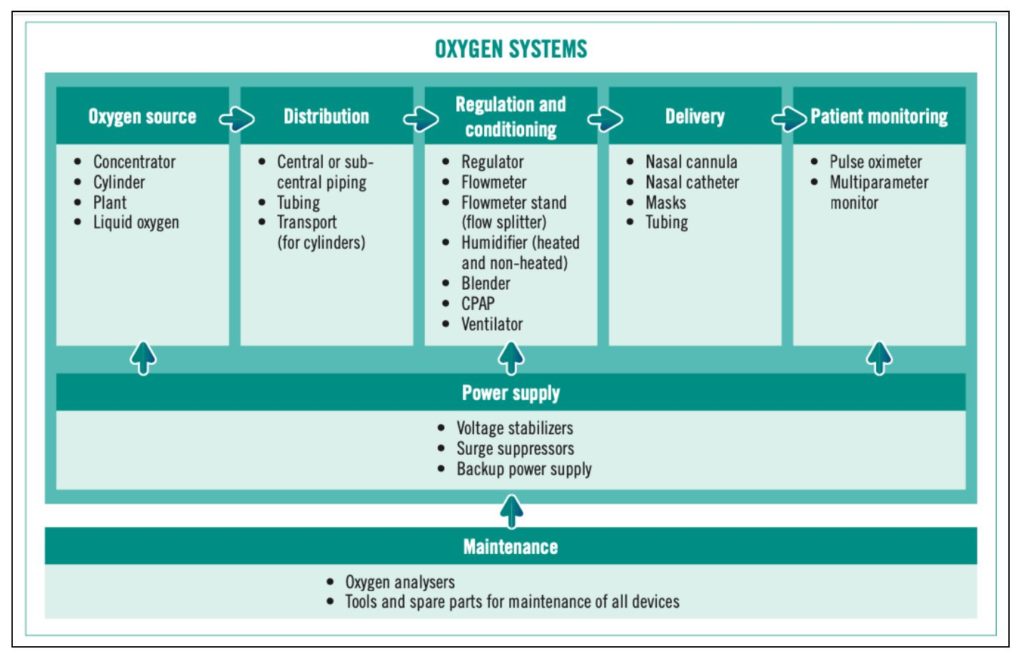
Oxygen Source forms the important component of any Oxygen system, as it is the main source from where the oxygen is being administered unto the patient. Depending on the requirement, capacity, and the settings, there are 4 major categories of Oxygen sources.
- Oxygen Cylinders
- Oxygen Concentrators
- Oxygen Plant (Central Oxygen Supply System)
- Liquid Oxygen Tanks
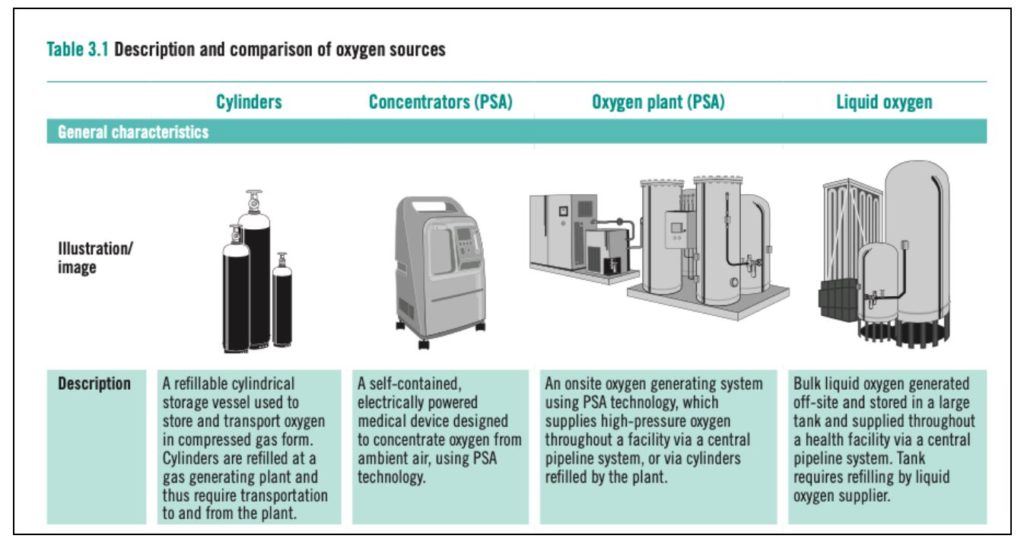
Among these, Cylinders & Concentrators can be set up in Low Resource Settings (LRS).
Oxygen Cylinders
Compressed Oxygen gas can be stored in cylinders. Oxygen is filled in these cylinders at a Gas manufacturing plant. This is done either through (a) Cryogenic distillation or (b) Pressure Swing Absorption (PSA).
These cylinders can either be used as part of a linked-up mechanism in health facilities or directly used for an individual patient.
- Logistics involved in the transport of the cylinders for regular refilling is one of the major challenges of opting for them. Few of the healthcare facilities overcome this challenge by refilling using any available PSA oxygen plant within the healthcare facility.
- Meanwhile, non-reliance on electricity is a major advantage offered by oxygen cylinders since they do not depend on a power source for the supply of oxygen. Nevertheless, various accessories & equipment are required to connect them.
- Because of the non-reliance on electricity, they are a preferred option in places with intermittent and unreliable power supply. They also offer a reliable backup where other oxygen systems are in place.
- While the initial setup costs are lower in the case of Oxygen cylinders when compared to other systems, the maintenance costs like refilling, transport, etc. can be high.
- Oxygen cylinders also are used in ambulances and the transport of patients.
Oxygen Concentrators
An Oxygen Concentrator is an electrically powered & self-contained medical device that can concentrate oxygen from ambient air. The Concentrator uses PSA i.e., Pressure Swing Absorption technology, to draw the air from the environment. It extracts Nitrogen and can produce 95.5% concentrated oxygen.
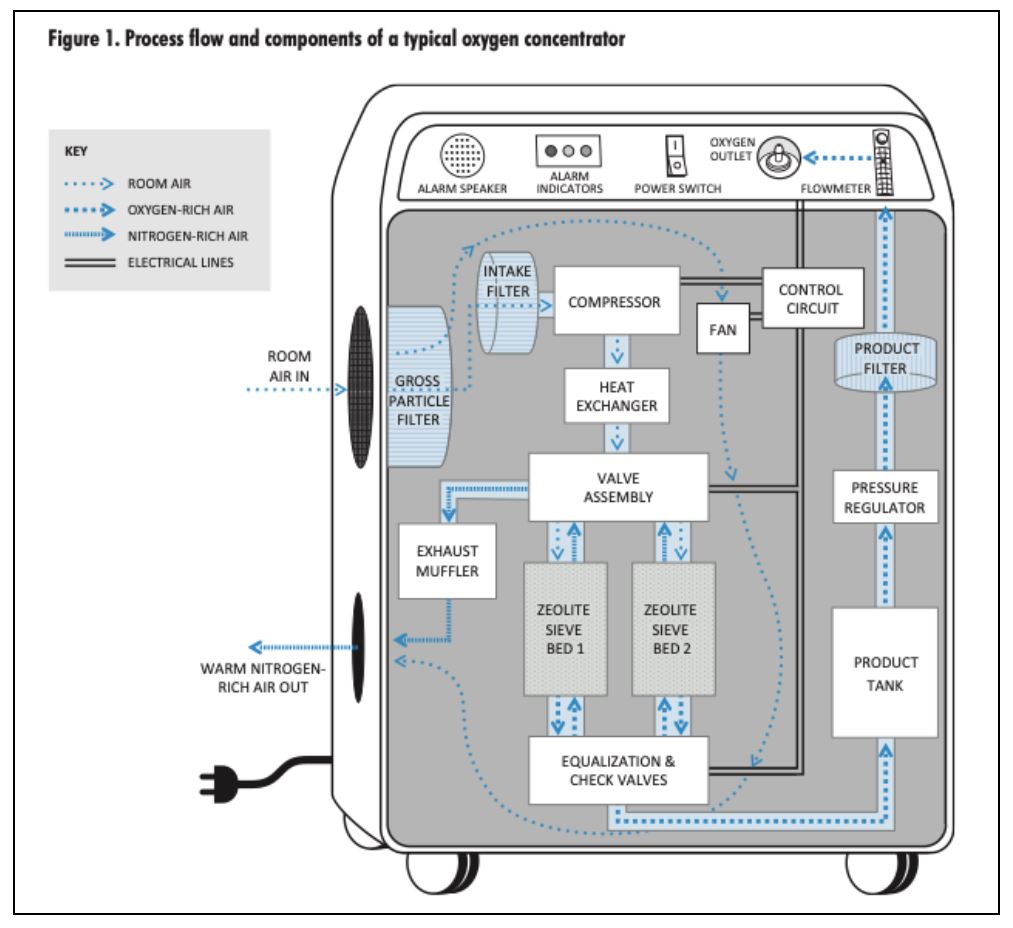
- The advantage offered by Oxygen concentrators is their portability. However, in most cases, they are set up as fixtures near the patients.
- Oxygen Concentrators are also designed for home or bedside care. Such Concentrators can deliver maximum flow rates between 5 & 10 L/Min.
- Using equipment such as a Flowmeter stand that splits the flow, the concentrators can provide a continuous supply of oxygen to multiple patients simultaneously.
- Most of the Oxygen Concentrators that are available in the market can produce Oxygen concentrations between 82%-96 % volume fraction.
- The challenge is with their continuous reliance on a power source. Hence, they are generally backed up by having Oxygen Cylinders in place.
Oxygen Plant
An Oxygen plant is an on-site Central source of oxygen. Here, oxygen is piped directly to the terminal units in the patient areas. They make use of either Cryogenic Distillation or PSA technology to generate oxygen. Similar to Oxygen Concentrators, even Oxygen Plants need a reliable source of power for proper functioning.
A pipeline system is connected to the Oxygen plants which facilitates the supply of oxygen at high pressures. Unlike a Concentrator which cannot be used to supply oxygen for machines such as ventilators, the Oxygen Plants can generate enough high-pressure oxygen to support ventilators, anaesthetic machines etc.
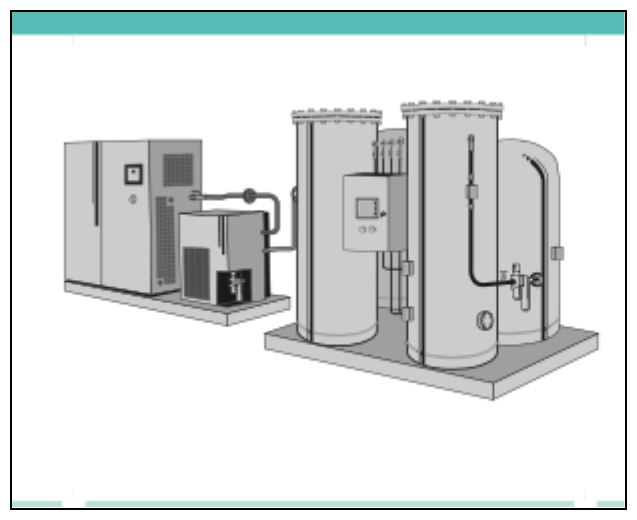
- As highlighted earlier, Oxygen plants can be used to refill oxygen cylinders. These could be stand-alone cylinders or the multiple connected systems in a healthcare facility.
- An Oxygen plant eliminates the cost and effort required in the logistics of transporting oxygen cylinders within the healthcare facilities.
- However, the higher costs involved in setting up an Oxygen plant make it a less preferred option in a low resource setting.
Liquid Oxygen Tankers
Another source of oxygen that can be set up at the health care facilities is Liquid Oxygen Tanks. These are large & bulky oxygen tanks that are periodically refilled by a supplier. The Liquid oxygen tank can supply oxygen to a centrally piped system that is set up in the healthcare facility. They use Self-Vaporization which eliminates the need for a power supply. However, the space required, and the technicalities involved in setting up such a system make them a less preferred option, especially in places that cannot afford such a facility.
Furthermore, the reliance on supply mechanism for refilling, makes it a less viable option especially in a country like India whose oxygen & gas supply delivery system may be required in less in low resource rural settings
Other equipment used for Oxygen supply
While the above systems act as the source of medical oxygen in a healthcare facility or to a home-based patient, there are other Oxygen Delivery & Monitoring systems like – flow meters, regulators, humidifiers, ventilators etc. that these are connected with in ensuring the delivery of oxygen to the patients.
Featured Image: Medical Oxygen Systems