[orc]Common Service Centers (CSCs) were initiated by the UPA government in 2006 with an aim of bridging the digital divide. As of 31st March 2016, close to 2 lakh CSCs are operational in the country with most of them in Uttar Pradesh.
The Common Service Centres (CSCs) were planned to bridge the existing digital divide by providing individual access to the internet and computer devices for the citizens in rural India. CSCs were envisioned to be well equipped ICT enabled centres enabling universal access to a host of eServices for citizens. The Phase I of CSC Scheme was launched in September 2006, during the UPA regime and the target was to cover all 6 lakh census villages by one lakh CSCs, as per 1:6 ratio equitably spread across rural India. As of 31st March 2016, close to 2 lakh CSCs are operational in the country with 36% of them in Uttar Pradesh and Maharashtra.
Services offered by CSCs
The following list of services are planned to be made available through the CSC network. CSCs in different states may offer only a few out of following.
G2C Services (Government to Citizen)
- Issue of various certificates, such as Caste, Income, Birth & Death, Land records, Domicile, etc.
- Employment Registration.
- Application for Ration Card, Application for pension (old age, widow etc), Application for Minority Scholarship/Girls Education Scholarship.
- PAN Card Services, Aadhaar Services, Election Commission of India (EC) Services, Passport Services.
B2C Services (Business to Citizen)
- Mobile / Data Card / DTH Recharge & Mobile Bill Payment.
- Electricity Bill Payment
- Tour & Travel (Booking for Air & Bus), IRCTC Service (through IRCTC authorized centres).
- e-Commerce service (Purchase of Various Products)
Educational Services
- Digital Literacy under National Digital Literacy Mission (NDLM)/Digital Saksharata Abhiyan (DISHA)
- Animation Course, English Speaking
- NIELIT Services and NIOS Services
Financial Inclusion Services
- Banking Services through Business Correspondents Agents
- Insurance Services of most of Insurance Companies as approved by IRDA (Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority)
- Pension Services of PFRDA (Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority of India) and other Government Schemes
Other Services
- Agriculture Service & Skill Development.
- Income Tax filing & Know Your TDS service.
- Health Care Services: Telemedicine, Jan Aushadhi and Diagnostic
- Swachh Bharat Abhiyan: Registration for Toilet Scheme
- Registration of Workers & Submission of Claims for Building and Other Construction.
CSCs are run by the Village Level Entrepreneurs (VLEs) selected by the relevant state and district agencies. The VLEs receive at least 80% of the income from the commission on various transactions. Preference is given to Women in the selection of VLEs. As of March 31st 2016, 23245 Women VLEs are operating the CSCs across the country.
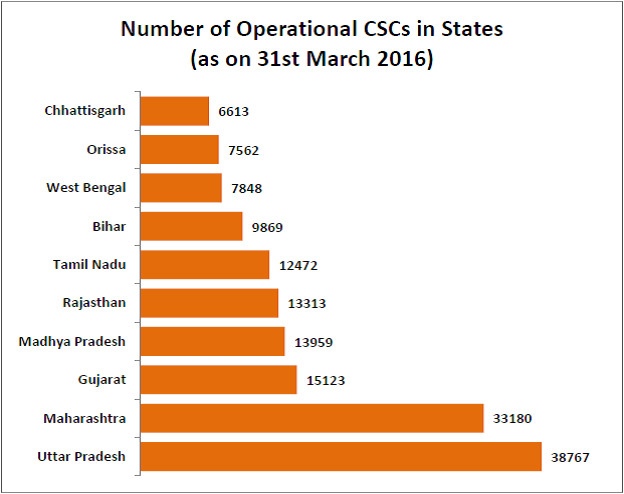
Close to 2 lakh CSCs operational in the country
As per the information shared by the government in the parliament, close to 2 lakh CSCs are operational in the country as on 31st March 2016. Uttar Pradesh has the highest number of operational CSCs followed by Maharashtra. Six states have more than 10000 operational CSCs while 12 states have more than 5000 operational CSCs. Goa does not have a single CSC. Of the bigger states, Telangana, Karnataka, Assam, Punjab and Kerala have less than 5000 operational CSCs.
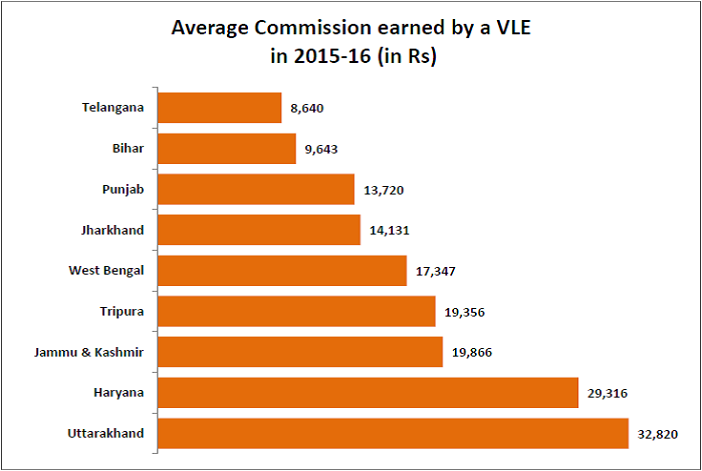
The average annual commission earned by a VLE is Rs 6141 in 2015-16
As per government data, a total of Rs 122.40 crore was earned as commission by the VLEs across the country in 2015-16. In terms of absolute amount, VLEs in West Bengal earned the highest commission in 2015-16 (Rs 13.61 crore) though the number of operational CSCs in West Bengal is only a fifth of the number in Uttar Pradesh. Other than West Bengal, only the VLEs in Uttar Pradesh earned more than Rs 10 crore as commission. But Uttar Pradesh is second from the bottom of all the bigger states when it comes to average commission per VLE in 2015-16. VLEs in Uttarakhand earned the highest average of Rs 32820. VLEs from only 7 states earned an average of more than Rs 10000 in annual commission while VLEs in twelve states earned less than Rs 5000 in annual commission. VLEs in states with the most CSCs (Uttar Pradesh & Maharashtra) earned the least average annual commission in 2015-16.
CSC 2.0 aims to reach all the Gram Panchayats by 2019
CSC phase two also known as CSC 2.0 aims to reach all the 2.5 lakh Gram Panchayats (GPs) by the end of 2019. More than 50000 GPs would be covered in Uttar Pradesh and more than 10000 GPs would be covered in each of the six other states.
Featured Image: CSC by Lingaraj33