[orc]Ever since the images & reports of Amazon forest fires came to light, there has been a renewed discussion on forest fires. But what is the status of forest fires in India? Here is a detailed analysis.
People from different parts of the world were taken aback when images and reports of Amazon forest fires came to light in the recent days. Even in the other parts of the world such as Africa, Europe and Asia, there have been severe forest fires off late. While global warming induced extremities in weather patterns have been associated with fires, there are also many human induced factors which pave the way for forest fires. In this story, we analyse the regional distribution and frequency of forest fires in India.
Number of Forest Fire incidents in India have increased in the recent years
Every year, there are numerous cases of forest fire incidents recorded across India. The data in the chart below contains forest fire incidents recorded up to June 2019. Hence the data for 2019 is incomplete.
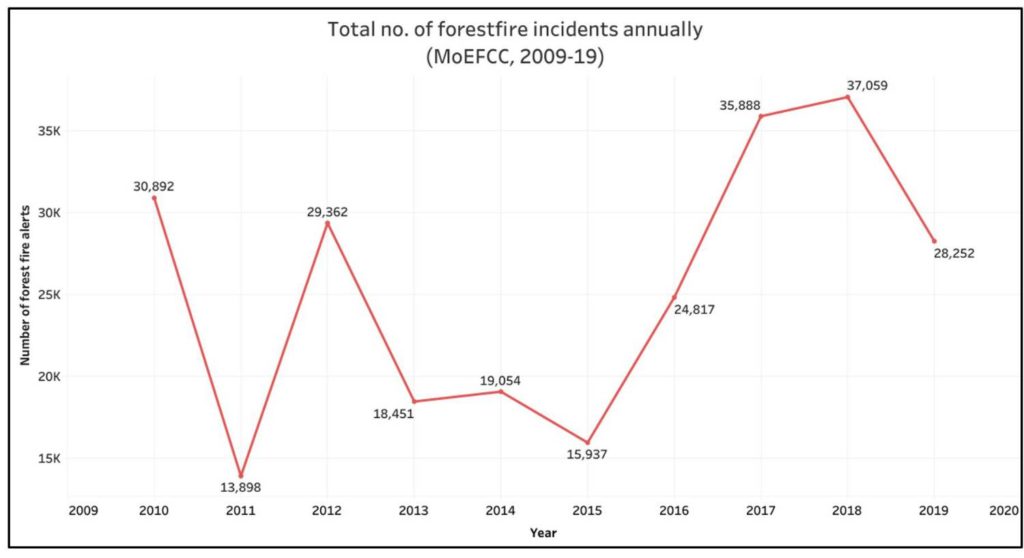
Though the graph looks highly staggered at the first glance, since 2015, the numbers show a stark increase in the number of such incidents. The cases have increased from 15,937 in 2015 to 37,059 in 2018 amounting to a shocking 133% increase. The 2019 figure is also expected to surpass the 2018 figure since we have the data only for 6 months.
Among the other years, the number of incidents in 2010 and 2012 were also remarkably high- 30,892 and 29,362 respectively. The Indian Meteorological Department reported in 2018 that 11 of the 15 warmest years recorded in India since 1901, were between 2004 and 2008. The report further noted that 2018 marked the sixth warmest year with 2016, 2009, 2017, 2010 and 2010 being the top five hottest years in that order. The years 2009, 2012 and 2016 were recorded as drought years in India as per the Forest Survey of India.
In the Forest Fire Alert system website of the Forest Survey of India, in 2019, the largest number of fire alerts was sent in the months of March and April. Since, November 2018, Madhya Pradesh, Mizoram, Maharashtra, Odisha and Assam in the same order are the top five states with the largest number of fire alerts till date.
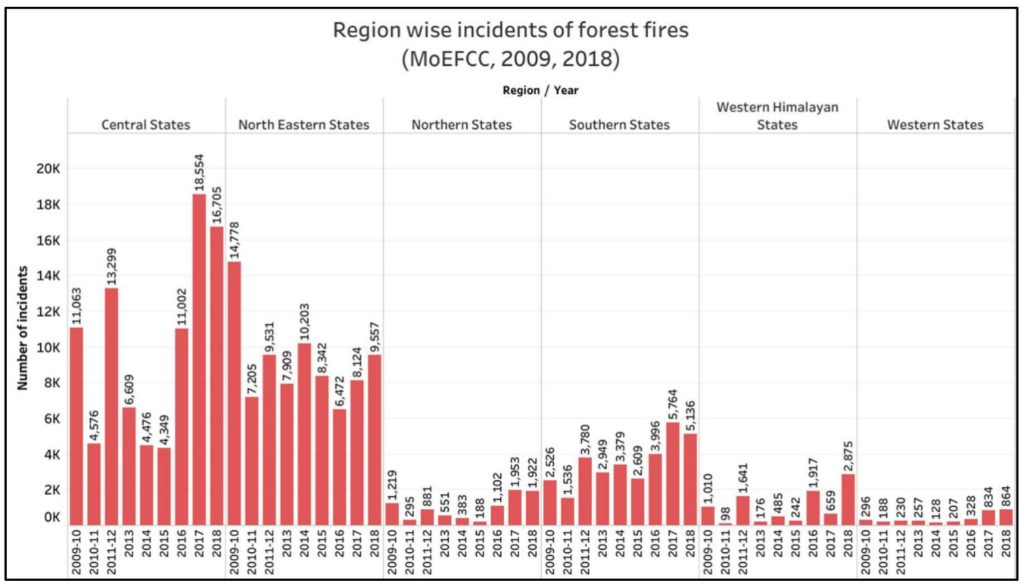
Central Indian states and North Eastern states together account for 76% of the Forest Fire incidents in the last decade
For the purpose of this analysis, states and union territories have been categorised into six regions. This grouping is based on the categorization given in the Forest Survey of India report.
| Region | States & UTs |
|---|---|
| Southern States | Andhra Pradesh, Goa, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Telangana, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Lakshadweep and Puducherry |
| Himalayan States | Himachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir and Uttarakhand |
| Northern States | Bihar, Delhi, Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh and Chandigarh |
| Western States | Gujarat, Rajasthan, Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu |
| Central States | Chhattisgarh, Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Jharkhand, Odisha and West Bengal |
| North Eastern States | Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim and Tripura |
As per the data available for the last 10 years, the Central Indian states are more prone to forest fires. About 40% of the cases of forest fires reported since 2009 have been in Central India. Not far behind, the North Eastern states where shifting cultivation is still prevalent account for 36% of the incidents. On the other hand, the Southern states account for 14% of the incidents, Western states for 1.5%, Northern states for 3.8% of the incidents and Himalayan states accounted for 4% of the incidents. The Forest Survey of India has reported that the maximum number of incidents has been reported in ‘Tropical Moist Deciduous’ forests. This is followed by ‘Tropical Dry Deciduous’ and ‘Tropical Semi- Evergreen forests’.
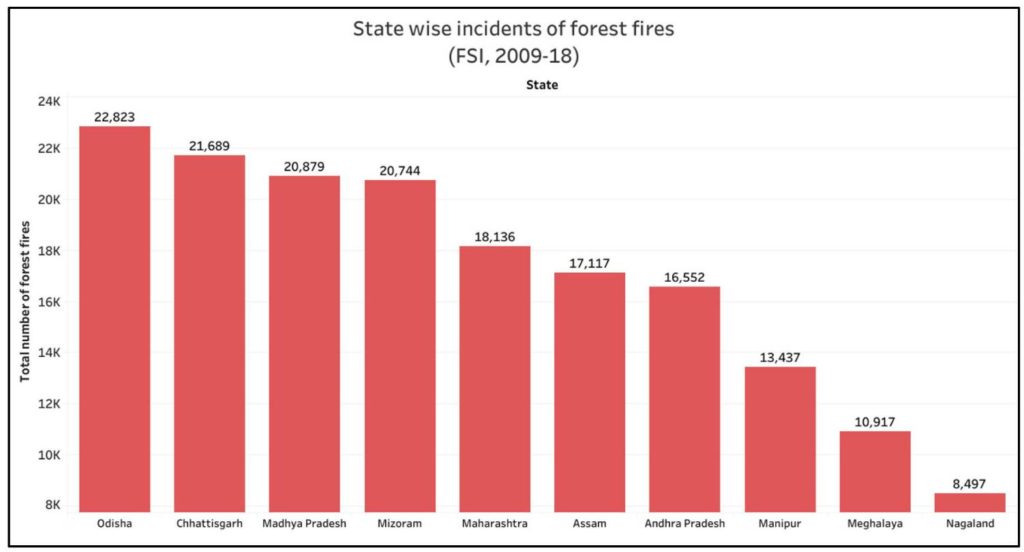
Odisha recorded the largest number of Forest Fire incidents between 2009 and 2018
State wise analysis of the total number of forest fire incidents between 2009 & 2018 reveals that the largest number of incidents was reported in Odisha with almost 23,000 incidents. Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh and Mizoram have also each recorded 20,000 incidents of forest fires during this period. Following the bifurcation of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, the number of incidents which have been recorded under Andhra Pradesh earlier has come down. The combined number of forest fire incidents in these two states during this period is 22,424 which is the second highest. In the following chart, the top ten states in terms of number of forest fire incidents reported since 2009 have been listed.
In the last three financial years, from 2016-17 to 2018-19, a total of ₹ 125 crores has been released for providing financial assistance to the states and union territories that were affected by forest fires. During the same period, land area of 180,342 hectares was affected. A total of 21 people lost their lives in related incidents in 2018 and one died in 2019. In addition to this, economic loss of around ₹ 10 crores was also estimated.
What is the National Action Plan on Forest fires?
Forest fire prevention and management fall under the state’s purview. Each state government and state forest department have their own forest fire management plans. The Ministry of Environment provides financial assistance to the states for the different measures taken by them which fall under the Centrally Sponsored Forest Fire Prevention and Management Scheme such as creation and maintenance of fire lines, storage of water in forest areas, appointment of firewatchers, purchase of necessary equipment, awareness, involving the communities living in these areas and conservation of soil.
Forest Survey of India has also developed an SMS warning system which sends fire alerts based on satellite data to those registered. The government has also come up with a National Action Plan on Forest Fire which addresses the actions to be taken pre and post forest fires. The Ministry also released a report in October 2018, made in collaboration with the World Bank titled ‘Strengthening forest fire management in India’ claiming that it would help India attain its long term climate change goal. The report discusses the policies on forest fire prevention and management and how to fight forest fires. According to this World Bank report, every year, India faces a loss of ₹ 1,100 crores because of forest fires. The social and ecological losses are also in plenty. The report stresses on the need for formulating appropriate policies involving proper guidelines and framework to deal with forest fires and forest management.
Sustainable Forest management is the need of the hour
Forest fires can occur unintentionally, due to natural reasons such as reduced moisture and high temperatures or ignorance of the people or deliberately when people set forests ablaze in order to acquire land for cultivation or to encroach. Recurring forest fires in short intervals have significant implications on the biodiversity. Though, it aids in regeneration of ecosystem, increased frequency will dwindle the biodiversity- both flora and fauna. The communities living in fringes of forests or within forests are highly susceptible since their lives as well as their livelihood are at stake when forests burn. Fires can also affect the crops grown on the adjacent plots. Sustainable forest management system needs to be implemented with the involvement of local communities in order to ensure that their needs are addressed simultaneously ensuring conservation of forests and biodiversity.
Featured Image: Forest fires in India



1 Comment
Pingback: What is the status of Forest fires in India? - Fact Checking Tools | Factbase.us