[orc]Government data indicates that the inhuman profession of Manual Scavenging still exists in the country and that there are more than 11000 such manual scavengers in the country. 86% of them are in Uttar Pradesh alone. There are 11 states which have manual scavengers even today. Despite the parliament enacting a legislation to prohibit manual scavenging, it goes on and the funds allocated for rehabilitation are hardly spent.
Not many of us clean our own toilets. The stench of toilets in public places puts us off. But there is another side to all of this. India still has people who are in the profession of Manual Scavenging. It’s a national shame, but it is also a fact that there are still a few thousand people engaged in the same.
The Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment defines a scavenger as the one who is partially or wholly engaged in the obnoxious and inhuman occupation of manually removing night soil and filth. The dependent of Scavengers is one who is a member of their family or is dependent of them irrespective of the fact whether they are partially or wholly engaged in the said occupation. The definition doesn’t necessarily capture the horrific nature of this work.
To explain in simple terms, manual scavenging refers to the removal of human waste/excreta (night soil) from unsanitary, dry toilets (toilets without the modern flush system). Manual scavenging involves the removal of human excreta using bare hands, brooms and tin plates.
The reality is much more inhuman and beyond imagination. The people who are involved in cleaning the dry latrines do so with their bare hands and usually carry the human excreta on their head to dispose in far off places. They are further ostracized, subjected to gross discrimination and have to go through everyday humiliation in society. Due to the nature of the work, they are also exposed to various health hazards. What is even more despicable is that this work is forced upon the future generations.
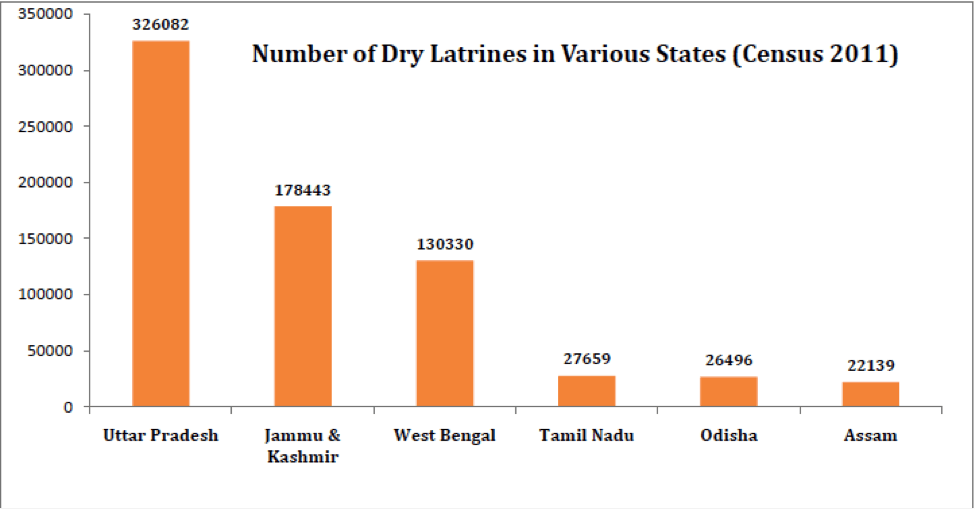
Dry Latrines
The presence of dry latrines is one of the primary reasons why manual scavenging exists till date despite being banned under the constitution via various legislations. As per the 2011 census data, latrines from which night soil is manually removed exist in all states except for the states of Goa, Sikkim and the UTs of Chandigarh and Lakshadweep. There are a total of 7,94,390 dry latrines in the country with Uttar Pradesh having as high as 3,26,082 and Andaman islands as low as 11.
Uttar Pradesh, Jammu Kashmir & West Bengal together account for 80% of all the dry latrines in the country. Nine states have more than 10000 dry latrines each and Ten States/UTs have less than 1000 dry latrines each.
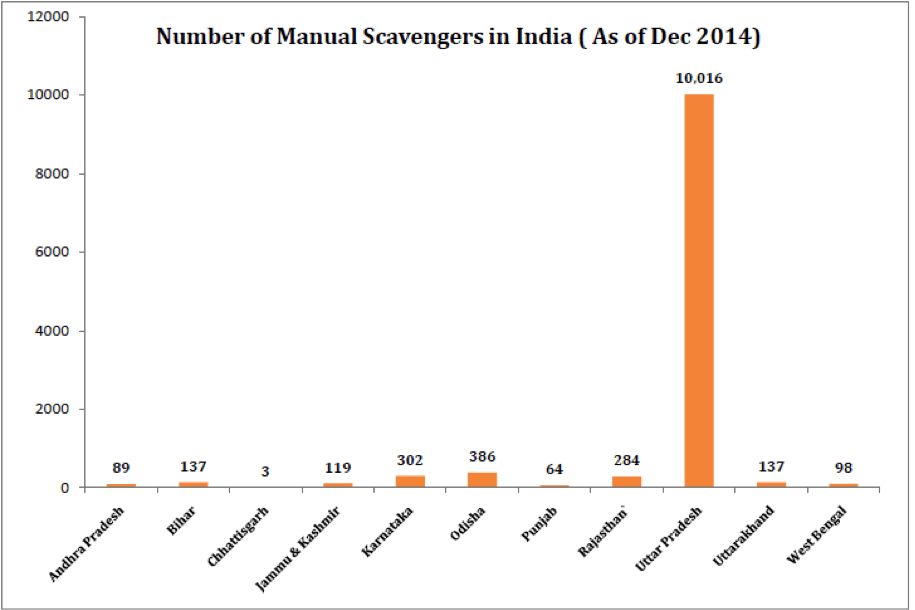
Number of Manual Scavengers
Not all states have Manual Scavengers. As per the latest data available with the Government, there are a total of 11,635 manual scavengers across the country. Leading the pack is Uttar Pradesh with 10016 manual scavengers. This is a whopping 86% of all manual scavengers in the country. There are 11 states where there are manual scavengers even today. These states are from all the parts of the country.
Current laws on Manual Scavenging
The current laws had not proved adequate in eliminating the twin evils of insanitary latrines and manual scavenging. The Parliament has enacted the ‘Prohibition of Employment as Manual Scavengers and their Rehabilitation Act 2013’. The law has come into force on Dec 6th 2013 in whole of country, except Jammu & Kashmir. The act intends to
- Eliminate the insanitary latrines.
- Prohibit
- Employment as Manual Scavengers
- Hazardous manual cleaning of sewers and septic tanks.
- Survey of Manual Scavengers and their rehabilitation
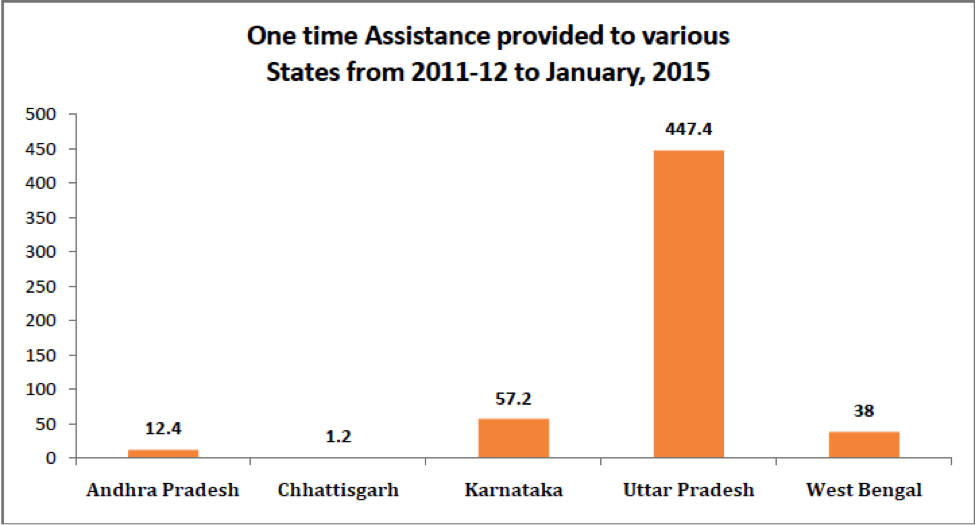
The act also has provisions for the following measures for the rehabilitation of the identified manual scavengers
- An initial one-time cash assistance
- Scholarship to the children of manual scavenger
- Allotment of residential plot and financial assistance for house construction of a ready built house
- Training in a livelihood skill with payment of stipend of at least Rs 3000 per month
- Provision for subsidy, along with concessional loans, to at least one adult member of the family
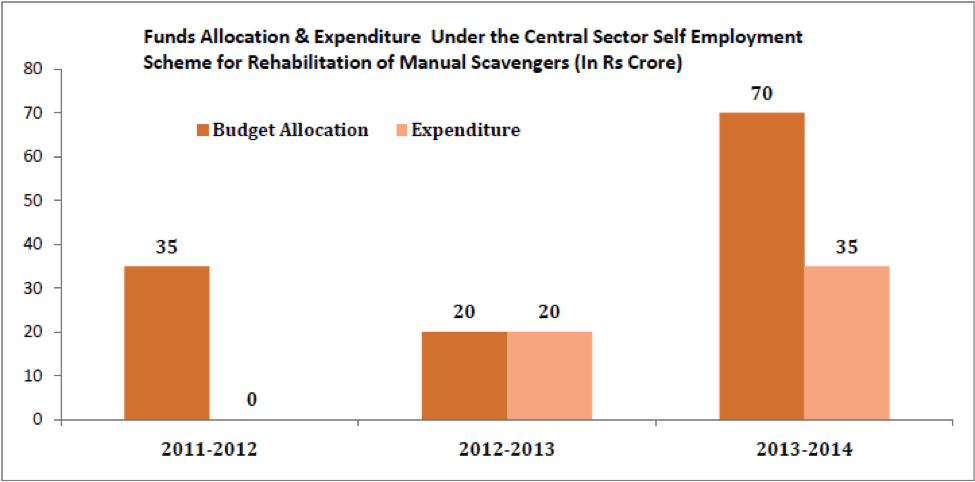
In addition to this, Central Sector Self Employment Scheme for Rehabilitation of Manual Scavengers is being implemented for rehabilitation of manual scavengers through the National Safai Karamcharis Finance and Development Corporation. Under this scheme, the fund allocated and utilized during the last three years is represented in the below chart.
The tragedy is that the government is unable to spend the meager amounts allocated for the rehabilitation of Manual Scavengers. In 2014-15, 448 crore rupees was allocated and not a single rupee has been spent till the end of July 2014. But can the rehabilitation programs really make an impact? The problem of manual scavenging is very deep rooted in the society. Once someone gets branded as a scavenger, the tag remains forever. Everyone in the neighborhood knows about their past and switching to a different line of work doesn’t necessarily help in making them more acceptable to the society. Along with these programs, there is a great need for sensitization and awareness to end this menace once and for all.
Sources
- Lok Sabha Unstarred Question No. 2688 answered on 9.12.2014, Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment
- Lok Sabha Starred Question No. 395 answered on 5.8.2014, Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment
- RTI reply from Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment
- Lok Sabha UnStarred Question No. 2096 answered 10.3.2015, Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment
Featured Image Source: By Dalit Network (http://www.dalits.nl/manualscavenging.html) [CC BY-SA 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons



6 Comments
Does this represent the number of manual scavengers employed with state governments or authorities constituted under it? Or does it represent the total number of manual scavengers per se in India?
Since Manual Scavenging is prohibited by law, states are not supposed to employ anyone to do this. There might incidents of local authorities using people. This number represents the total.
but the ones existing today who are employing them? Is it because these families don’t know any other skills to earn livelihood? extreme poverty is the only reason for sure. and there are deeper issues like alcoholism which makes the men folk do anything for quick money.
Pingback: Govt Jobs Portal Has Listed Manual Scavenging As A Job, Despite It Being Illegal
Pingback: Govt Jobs Portal Lists Manual Scavenging As A Job, Despite It Being Illegal -
Pingback: Why India Hasn't Been Able to Get Rid of Manual Scavenging | Indians 4 Social Change