[orc]Every Vehicle bought in the country has to be registered with the Regional Transport Authority (RTA) who in turn allots a registration number. But what does the Registration Number indicate and how are these numbers allotted?
Every vehicle bought in the country has to be registered with the local Road Transport Authority (RTA) following a due process. The application for registration has to be submitted along with the requisite documents, and the prescribed fee for registration. The RTA in turn registers the vehicle and allots a registration number to the vehicle. But how is this registration number allotted? Here is a detailed explanation of the registration number and what it means.
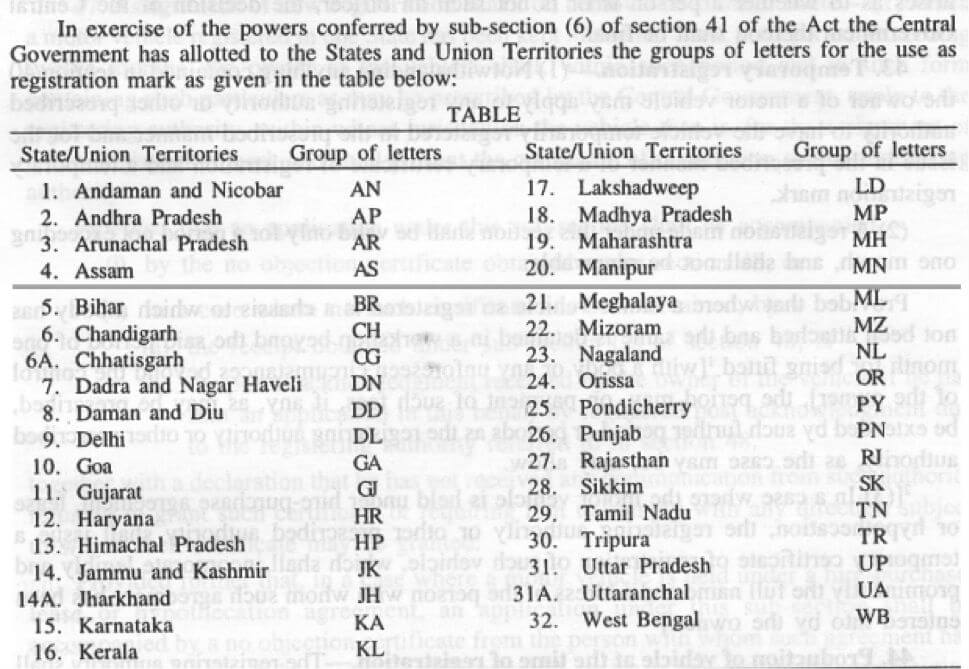
The State Code (The first two letters)
The first two letters of any registration number indicate the state or the union territory. Section 41(6) of the Central Motor Vehicles Act, 1988 authorizes the central government to allot two letter codes for each state or union territory. Vehicles of Diplomatic Officers, United Nations Personnel are registered separately. The state of Telangana has been added to this list in 2014 with the code TS.
Note: The above screenshot is from the Ministry of Road Transport & Highways, Government of India and there seems to be a mistake in the code for Punjab. The code for Punjab is ‘PB’ and not ‘PN’.
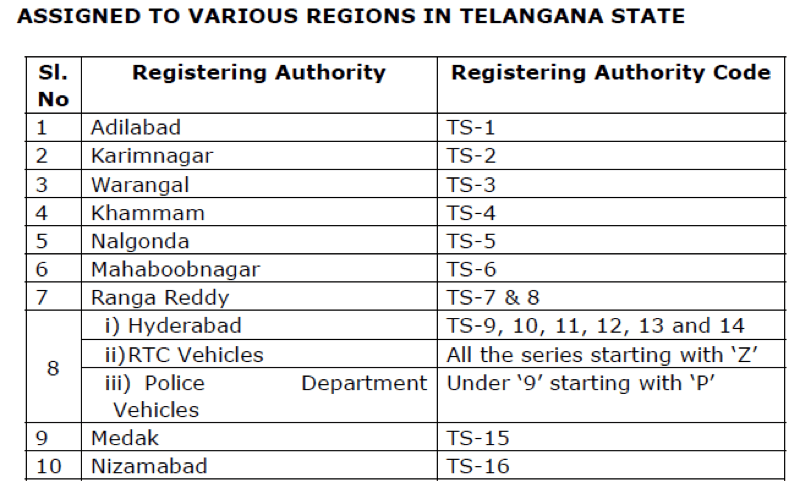
Registering Authority (The next two digits)
The two digits next to the State/UT code represent the code of the Registering Authority. The registering authority is usually a district. The relevant state government is authorized to allot these codes. Certain districts or registering authority may be given multiple codes (for e.g., capital cities, metros etc), since a large number of vehicles are bought in these places.
For example, Rule 80 of the Telangana Motor Vehicles Rules, 1989 authorize the government of Telangana to allot codes to the registering authorities. Similar allotment is done by all state governments.
The Alphabetical Series (The Next two letters)
The next two letters represent the alphabetical series that starts from A and can technically go up to ZZ. Certain alphabets are reserved for registration of specific category of Vehicles. For e.g., in Telangana, the series starting with Z in Hyderabad is reserved for the Road Transport Corporation vehicles. Similarly, the series starting with P is reserved for Police Vehicles. The series with T,U,V,W,X and Y are reserved for Transport Vehicles.
The Last Four Digits
For alloting the last four digits, the applications received on a given day are arranged in alphabetical order and the numbers are usually allotted serially after the last registration number assigned the previous day.
The authority reserves the right to reserve certain registration numbers that are considered fancy or rare. These numbers are allotted on payment of an additional fee. For e.g., in Telangana, numbers 1, 9, 999, 9999 are allotted on payment of an additional amount of Rs 50,000.
But if there is more than application on a particular day for a specific number, then offer amounts in closed envelopes are invited form the applicants. The applicant offering the highest amount is given that number, provided it is not less than the minimum specified amount.
Certain Numbers are also reserved for government vehicles.
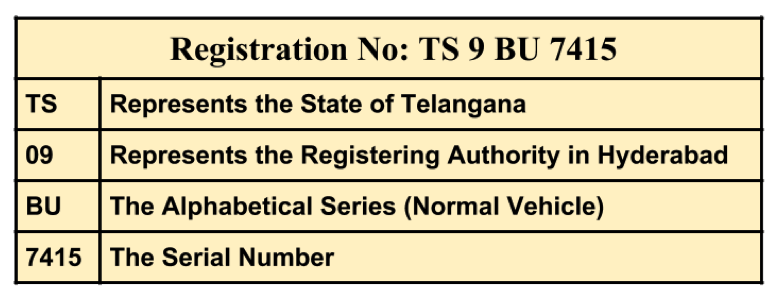
Example Illustration




4 Comments
Hi Rakesh, really nice article. How can one find the rules that associate the ‘Alphabetical Series’ with the specific category of Vehicles? I imagine these would be different in each state? Thanks.
Please check the relevant motor vehicle rules of the state governments
Pingback: How the UK Number Plate System Works - WhiteOut Press
what after zz series ?