The NFHS-5 provides data on internet usage for the first time. As per the available figures, less than 30% of the rural women have ever used the internet in 10 states. While most states have reported improvement in access to an improved sanitation facility, data indicates that the majority of the rural households are still sourcing drinking water from a public facility.
The National Family and Health Survey (NFHS) provides estimates on various key indicators relating to the population, health, nutrition, etc. The recently published factsheets of 22 States/UTs under Phase-1 of NFHS-5 offer insights on a variety of important aspects of family well-being. In our earlier stories, we covered some important observations regarding a few of these key indicators from NFHS-5.
Access to various facilities is an important component of family well-being. The provision of basic facilities to its population is also key to a welfare state. Over the years, access to various basic facilities has improved across the country. However, disparities exist among the various regions and sections of the population.
In this story, we take a look at access to a few of the basic facilities based on the data provided by NFHS-5 for the 22 States/UTs covered under phase-1.
Less than 30% Rural Women ever used Internet in 10 States
It is estimated that India has the second-highest number of Internet users in the world, second only to China. However, this accounts for just more than a quarter of India’s population, as per the data available in 2015. The indicator ‘Men/Women who have ever used the Internet’ was introduced for the first time in the latest NFHS- 5 survey.
Among the 22 States/UTs that are part of Phase-1 of the survey, Goa has the highest share of men who have used the internet with around 83% while Sikkim has the highest share of women who ever used the internet with around 77%.
Among the states with a large population, Kerala tops the list with around 76% men and 61% women that have ever used the internet respectively.
- Kerala, Jammu & Kashmir, and Himachal Pradesh are the only larger states which are estimated to have more than half the population that has ever used the internet.
- When only the Male population is considered, Gujarat, Karnataka, Maharashtra & Telangana join the aforementioned states with an estimated more that 50% that have ever used the internet. Meanwhile, Andhra Pradesh, Assam, Bihar are among the larger states with less than 50% of the male population that has ever used the internet.
- With the exception of Kerala & Himachal Pradesh, most of the other states with a sizable population have a lower share of women who have ever used the internet.
- The difference between men and women is stark in Telangana & Gujarat which have comparatively higher coverage among men but are among the states with a lower share of women who have ever used the internet.
- Only around 21% of the women (15-49 years) in both Andhra Pradesh & Bihar have ever used the internet.
Data indicates a consistent trend among all the States/UTs with a higher share of urban men that have ever used the internet. Barring a few exceptions, a very low proportion of rural women have ever used the internet in a large number of states. In fact, this proportion is less than 30% in 10 of the 17 states part of the first phase of the NFHS-5.
The disparity between the States can also be observed in the data provided by the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI). As per its latest Quarterly Report – The Indian Telecom Services Performance Indicators for April-June’2020, Kerala has around 77 internet subscribers per 100 population. Himachal Pradesh has around 82 internet subscribers per 100 population.
Andhra Pradesh, which also includes Telangana as per the TRAI report has around 66 internet subscribers per 100 population. While the criteria are different both for TRAI data and the estimates as per NFHS-5, a general trend is observed that Bihar and Wes Bengal are among the states with a lower share of internet subscribers. While NFHS-5 estimates the number of people who have ever used the internet, TRAI data is based on the subscriber information from the telecom companies.
Population in most states report improved Sanitation facility
As per the information updated on the Swachh Bharat Mission portal, India is declared to be 100% Open Defecation Free (ODF). As per the National Annual Rural Sanitation Survey 2019-20 (NARSS), 94.4% of Rural Households have access to toilets. Of these, 79.2% of households have access to their own toilet.
One of the key indicators under NFHS-5 is ‘Population living in households that use an improved sanitation facility’. Any household reporting the following in its own household is counted under this indicator.

Less than 50% of the population reporting an improved sanitation facility in only Bihar & Ladakh. In the rest of the states/UTs part of the first phase of NFHS-5, this is more than 50%.
However, there is a considerable improvement even in these two with over 20% improvement from the previous survey. The best improvement compared to the previous survey is seen in Telangana with nearly 24%.
A lower proportion of the population living in households with improved sanitation facilities as estimated in NFHS-5, when compared to the ODF numbers on the Swachh Bharat Mission portal is an indication of the issues with access to individual toilet units that are being used.
Majority of the rural households still sourcing drinking water from a public facility
Access to clean drinking water is one of the basic needs for sustainable living. As per the criteria specified in NFHS-5, a population who have access to piped water directly to their homes, or access to a clean water source with the neighbours or within the neighbourhood, are deemed to have access to an improved drinking water source.
As per the fact sheets as part of NFHS-5 for the 22 states/UTs of Phase-1, with the exception of few northeastern states, more than 90% of the population has reported access to the improved drinking water sources in the rest of the states. The improvement is not as much compared to sanitation facilities since more than 90% of the population reported access to improved drinking water sources even in NFHS-4 (2015-16).
As per the Ministry of Jal Shakti’s Jal Jivan Mission’s Dashboard, about 33% of the rural households have Functional Household Tap Connections (FHTC). As per the information, the number has nearly doubled compared to 15 August 2019, the date on which the scheme was launched.
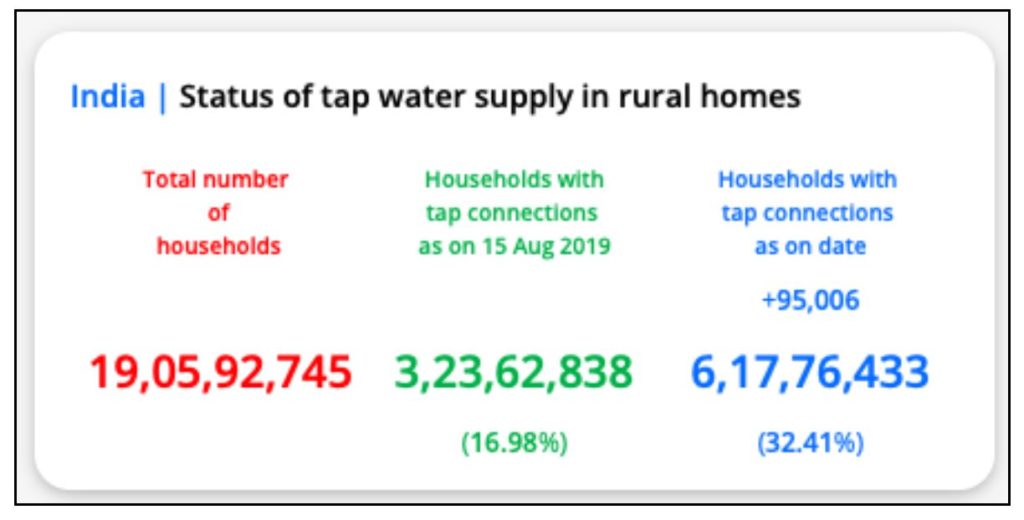
The estimates for NFHS-5, indicate that an average of more than 90% rural population in these 22 states/UTs have access to improved drinking water sources. The lower FHTC in these states could be due to the fact that the majority of the population in rural areas source drinking water from a public facility rather than from a household tap.
Featured Image: Access to basic facilities


